Microplastic Detox: Uncovering the Hidden Plastics in Beauty Products
A Microplastic Detox You Need To Know About!
Discover the Hidden Dangers of Microplastics in Your Daily Beauty Routine
Did you know your daily beauty routine might be contributing to a global issue? Yes, microplastics, those tiny particles smaller than a grain of rice, are lurking in your favorite cosmetics, body washes, and even toothpaste.
Used as a cheaper alternative to natural exfoliants, these minuscule plastics are not only harmful to the environment but could also pose risks to your health.

The Unseen Threat in Your Toothpaste
Take a closer look at your toothpaste. See those sparkling little blue dots? They might be microplastics, specifically polyethylene. This form of plastic, the most popular worldwide, adds that glittery look but at a significant environmental and health cost. Seems insane this is not illegal but greed rules the day, and your health is just not important to the companies who use this.
The Truth About Face and Body Washes
Feeling clean might come at a hidden price. Face and body washes often contain polypropylene microbeads. These tiny plastic particles act as exfoliants, but they eventually find their way into our waterways, contributing to pollution in rivers, lakes, and oceans.

Cosmetics: A Plastic Beauty
Almost every makeup product, from blush and foundation to mascara and lipstick, might contain plastics. The list include the likes of polyethylene, polypropylene, or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Even the glitter in your makeup is essentially tiny pieces of plastic. People are adding to microplastic pollution with every use of these products.
The Impact on Health and Environment
Before these microplastics wash down the drain, they can pose significant health risks. Inhaling microplastics has been linked to asthma, heart disease, and even cancer. Recognizing the threat, the United States introduced the Microbead-Free Waters Act in 2015, aiming to reduce the use of microbeads in cosmetic products. Notice the word “reduce” and not stop. So buyer beware!
Making a Difference with Microplastic Detox
As consumers, we play a crucial role in combating microplastic pollution. By choosing products without polyethylene, polypropylene, or PET, we can make a more environmentally friendly choice. Opting for natural alternatives not only benefits the planet but also supports our well-being.

Chelanox by Bionox: Your Ally in Microplastic Detox
In your journey towards a microplastic detox, consider integrating products like Chelanox by Bionox into your routine. This innovative solution supports your body’s natural detoxification processes. It works by helping to mitigate the impacts of environmental pollutants, including microplastics. By choosing environmentally friendly products and supporting your body’s health, you can make a significant difference for both your well-being and the planet.
A Call to Action
Living entirely without plastics might be a daunting task, but being mindful of our choices can lead to substantial positive changes. Next time you’re shopping for beauty products, take a moment to read the labels. Opt for products that are free from harmful microplastics and consider how your daily routine can contribute to a healthier planet. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against microplastic pollution.

Chelation Therapy and Heart Disease: A Deep Dive into Potential Benefits
Chelation Therapy and Heart Disease. Cardiovascular disease remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. With myriads of available treatment options, a less-known but intriguing approach has emerged: Chelation Therapy.
Rooted in its primary use for heavy metal poisoning, chelation for heart disease has garnered attention, thanks in part to studies like the TACT (Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy). This article delves into the potential benefits of chelation therapy for heart disease, anchoring our exploration in the findings of the TACT.
Understanding Chelation Therapy
Before we proceed, it’s essential to grasp what chelation therapy entails. At its core, chelation involves the administration of chelating agents that bind to metal ions in the body. This process facilitates the removal of these metals, initially used to treat heavy metal poisoning. The keyword here is ‘bind’: the chelating agents ‘grab’ these metals, allowing them to be safely excreted.
Research has explored the idea that chelation might also bind to calcium deposits in the arteries. The hypothesis? By reducing calcium-based plaque build-up, there’s potential to improve blood flow, addressing one of the core issues in heart disease.
The TACT (Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy)
The TACT study is arguably the most comprehensive exploration of chelation therapy’s role in heart disease done to date. Initiated in 2003, this study was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid) chelation therapy in individuals with a history of myocardial infarction ( heart attacks ).
Promising Findings from TACT
Reduction in Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes:
The TACT indicated that chelation therapy could lead to a modest reduction in cardiovascular events. The findings suggested that those receiving chelation therapy experienced fewer subsequent heart issues when compared to the placebo group.
Beneficial for Diabetes Patients:
One of the most notable revelations from the TACT was the pronounced benefit observed among patients with diabetes. The trial showed that diabetic participants had a 41% relative reduction in the risk of any cardiovascular event and a 43% reduction in the risk of death from any cause.
Safety:
An essential facet of the TACT was its rigorous monitoring for potential side effects. The findings affirmed the relative safety of chelation therapy when administered under appropriate medical supervision.
Supporting data from the TACT provides a foundation for understanding how chelation therapy could play a role in modern cardiology, especially in specific subsets of patients like those with diabetes.

TACT2 Study
TACT2 was a study that looked at how EDTA chelation treatment might help heart health, especially for people with diabetes. Here’s what they found:
Blood Sugar Levels Stayed Stable:
This treatment didn’t seem to change people’s blood sugar levels much. Whether they were on the treatment or a placebo (a fake treatment), their blood sugar levels stayed about the same. No surprise here, really, though.
Diabetes Medication Needs Didn’t Change Much:
Most people with diabetes still needed the same amount of diabetes medicine after the study, whether they had the real treatment or the placebo. Again no surprise.
Heart Benefits for Those with Diabetes:
This is where things get interesting! People with diabetes who got the real treatment had fewer major heart problems. They did 41% better than those on the placebo.
There were also fewer other heart issues in the treated group.
In simple terms, TACT2 found that this EDTA chelation treatment might be a pretty good option for the hearts of people with diabetes.
The Mechanism: How Does Chelation Impact Heart Disease?
The underlying mechanism of how chelation affects heart disease is multifaceted. One dominant theory aligns with the chelation’s inherent action of binding metals. By reducing the metal-catalyzed oxidative stress, chelation therapy might prevent the oxidative modification of LDL cholesterol, a significant contributor to atherosclerosis.
Additionally, by removing calcium deposits, chelation might lead to the regression of plaque build-up in the arteries. This process would inherently improve blood flow, a crucial factor in cardiovascular health.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Chelation Therapy and Heart Disease
With the TACT providing a robust foundation, the intrigue surrounding chelation therapy in cardiology is undeniable. While the treatment isn’t mainstream, its potential benefits warrant further exploration, especially for specific patient groups.
Future studies might delve deeper into understanding which patient profiles stand to benefit the most. For instance, will the pronounced benefits observed in diabetic patients be replicated in larger, more diverse cohorts?
Why Chelanox Can Help with Heart Health
Ingredients & Research
Chelanox stands out in the world of chelation supplements because its potent ingredients specifically target and bind to heavy metals in the body, assisting in their removal. If left unchecked, these heavy metals can contribute to various health issues, including cardiovascular problems.
Ingredients in Chelanox:
EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid):
EDTA is a well-known chelating agent. A landmark study, the TACT (Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy) that we mentioned earlier found that a combination of EDTA and high-dose vitamin therapy significantly reduced cardiovascular events, particularly in diabetic patients.
Other Ingredients:
- Chlorella Algae: Chlorella is believed to have detoxifying properties, particularly in binding and eliminating heavy metals and other toxins from the body.
- Modified Citrus Pectin: A form of pectin that is altered to be more easily absorbed by the digestive tract. It has been studied for its potential ability to inhibit the spread of certain cancer cells and also for its chelating properties, particularly for lead, cadmium, and mercury.
- Cilantro Leaf Extract 4:1: Cilantro, also known as coriander, has been suggested in some studies to help eliminate heavy metals from the body, although this is an area of ongoing research.
- Shilajit 10:1 Extract: An ancient traditional medicine, shilajit contains fulvic acid and various minerals. It’s been proposed to have a potential role in detoxification and also boasts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Zeolite: Zeolites are minerals with a cage-like structure that can capture certain molecules, including some heavy metals, making them of interest in detoxification.
- NAC (N-Acetylcysteine): A powerful antioxidant that can boost glutathione levels in the body, a vital antioxidant for liver detoxification. It can also act as a chelator for heavy metals.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid: Known for its antioxidant properties, it helps protect the body’s cells from damage. It has also shown potential as a chelator for heavy metals.
- Uva Ursi Leaf Powder: Traditionally used for urinary tract infections due to its antibacterial properties, it can also have a diuretic effect helping to flush the kidneys and urinary system gently.
- Milk Thistle Seed Powder: Known for its liver-protective effects, it can boost liver health and assist in detoxification processes.
The blend of these ingredients in Chelanox suggests a combination of traditional chelating agents with herbal and natural components that have historically been associated with detoxification. The Chelanox formula supports the body’s natural detoxification processes, enhancing liver health, and possibly aiding in removing certain toxins, including heavy metals.
Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition by Bionox – The Perfect Pairing
Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition serves as a potent supplement that supports heart health. Nitric oxide is a molecule that plays a crucial role in vascular function, aiding in the dilation of blood vessels and promoting blood flow.
Ingredients & Benefits of Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition
L-arginine and L-citrulline:
These amino acids are precursors to nitric oxide. Studies, such as one published in the American Journal of Cardiology, have indicated that they can help improve endothelial function and potentially reduce blood pressure.
Antioxidant-rich components:
The Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition formula contains other ingredients, such as vitamins C, E, and D, that combat oxidative stress, which can damage the cardiovascular system. Many of the herbal ingredients, such as grape seed extract, also help in similar ways.
Combining Chelanox and Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition for Heart Health
Together, Chelanox and Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition can offer a two-pronged approach.
Detoxification with Chelanox:
By removing heavy metals, Chelanox can potentially reduce the toxic burden on the heart and vascular system. This process can also help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress these metals might cause.
Vascular support with Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition:
The heart doesn’t have to work as hard to pump blood as the blood vessels become more flexible and relaxed due to the increased nitric oxide levels. This can lead to better overall cardiovascular function and reduced risk of related issues.
To wrap things up, detoxification and vascular support are crucial when seeking a holistic approach to heart health. Combining Chelanox and Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition can harness a powerful duo that addresses heart health from multiple angles. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.

Unleash the Power of Oral Chelation Supplements: Understanding Heavy Metal Detoxification
In our increasingly polluted environment, it’s essential to explore innovative strategies to maintain our bodies in a state free from damaging toxins and impurities. Global pollution and ecological challenges have led to a surge of interest in oral chelation supplements. Particularly popular are those targeting heavy metal detoxification. Contaminated food, beverages, manufacturing processes, and pesticides can all contribute to an unwanted toxic burden.
It is essential to understand the methods for removing toxins from our bodies and the potential damage they can cause.
Prominent in the field of Chelation is Chelanox by Bionox®. Chelanox is a potent blend of botanicals engineered to counter the harmful impacts of heavy metals in our systems. We’ve meticulously researched each ingredient to curate the most effective formulation. Our goal today is to enlighten you about the intricacies of Chelation and the rationale behind our ingredient selection.
Exploring Oral Chelation
Oral chelation represents a health or dietary intervention that leverages certain compounds to purge the body of detrimental toxins, mainly heavy metals.
Known as chelating agents, these elements bind with the toxins and heavy metals inside the body. This helps the body detox by creating a stable chelate compound. The body then safely removes this compound through urine or feces. Initially used to fight against heavy metal toxicity, the application of this therapy has expanded over time.
The introduction of products like Chelanox has expanded its scope to encompass preventative health and overall wellness.
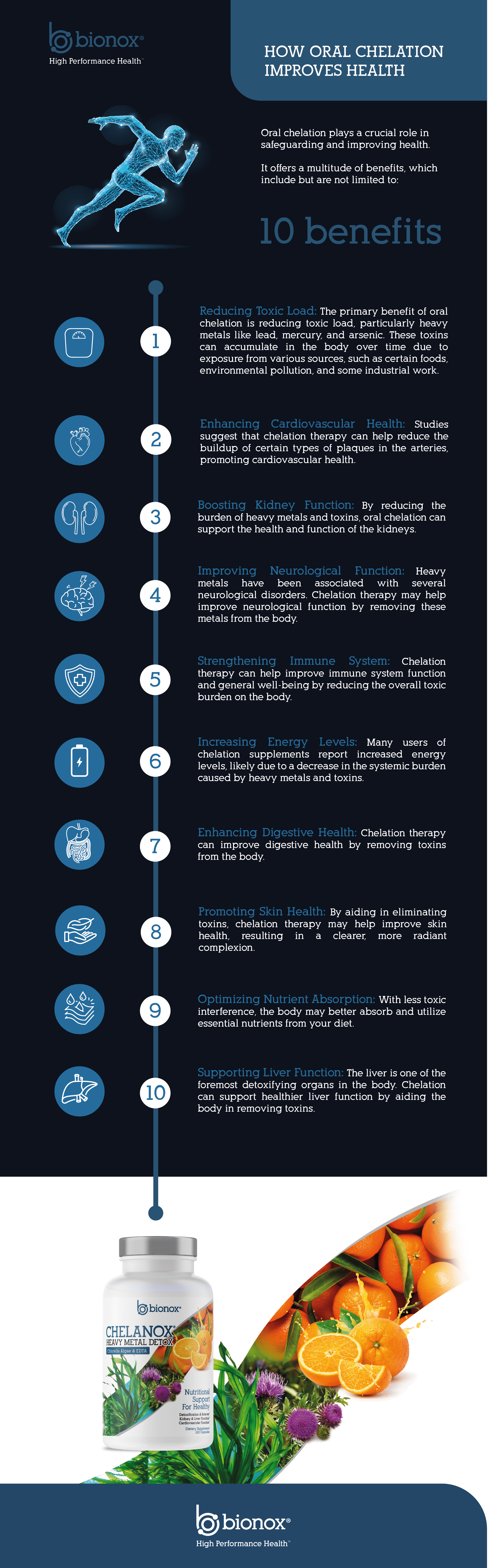
Oral chelation could play a pivotal role in protecting and elevating your health:
- Diminishing Toxic Burden – The main advantage of oral chelation is the diminution of toxic burden, primarily heavy metals like arsenic, lead, and mercury.
- Maintaining Heart Health – Research indicates that chelation therapy could decrease the accumulation of specific types of plaque in arteries, thereby facilitating optimal cardiovascular well being.
- Preserving Kidney Health: By alleviating the load of toxins and heavy metals, oral chelation products could help maintain the health of your kidneys.
- Preserving Neurological Function – Chelation therapy could help maintain neurological function by expelling heavy metals from your body.
- Immune System – Chelation therapy can boost immune system health and general vitality by lessening the total toxic load on the body.
- Boosting Vitality Levels – Chelation supplement users often report a surge in vitality levels. This is likely due to reduced systemic stress caused by toxins and heavy metals. Increased vitality leads to an overall better feeling and increased activity, which is always beneficial!
- Gut Health – Chelation therapy could bolster gut health by expelling toxins from the body.
- Enhancing Skin Health – Chelation therapy might boost skin health by facilitating the expulsion of toxins, leading to a cleaner, more glowing complexion.
- Maximizing Nutrient Uptake – Reduced toxic interference may allow the body to absorb and utilize essential nutrients from your diet more effectively.
- Maintaining Liver Health – The liver plays a key role in detoxification within the body. Chelation could foster healthier liver function by assisting the body in toxin removal.
Reducing toxic load
Let’s examine the key ingredients in our Chelanox product to understand their functions:
- EDTA Calcium Disodium. A study in the Journal of Advancement in Medicine found that oral intake of EDTA can be beneficial for reducing lead toxicity.1
- Chlorella Algae. A recent study published in Nutrition Research and Practice concluded that chlorella could decrease the amount of dioxin in breast milk and in the body generally. 2
- Modified Citrus Pectin. MCP is a type of pectin that has been altered to be more easily absorbed by the digestive tract. A study in Phytotherapy Research indicated that MCP can help reduce lead levels in the body. 3
- Cilantro Leaf Extract. A study that was published in the Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine suggests that cilantro can expedite the body’s excretion of lead and mercury. 4
- Shilajit. Shilajit is rich in fulvic and humic acids, which may possess chelating properties, according to a study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 5
- Zeolite. Zeolites are volcanic minerals that can act like magnets for toxins. Research has shown that zeolite clinoptilolite can trap and remove harmful toxins, including heavy metals, from the body. 6
- N-Acetyl Cysteine. Is known to enhance the production of glutathione. 7
- Alpha Lipoic Acid. ALA is a potent antioxidant that can bind with toxic free radicals and help remove them from the body. A study in Free Radical Biology & Medicine found that ALA can help the body detoxify from heavy metals. 8
- Uva Ursi Leaf and Milk Thistle Seed . These ingredients, traditionally used in herbal medicine, are included for their diuretic and liver-supporting properties, respectively, thus aiding in the detoxification process. 9, 10
How does oral chelation enhance heart health?
Chelation therapy has been studied for its potential benefits in treating cardiovascular disease, mainly by addressing atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaques in the arteries.
These plaques, primarily comprised of cholesterol, fat, and calcium, can restrict blood flow and potentially lead to severe cardiovascular events like heart attack or stroke.
While the mechanism isn’t entirely understood, some theories suggest that the calcium-disodium form of EDTA could bind with the calcium in these plaques, thus helping to reduce their size and improve blood flow. For this reason, we use this form of EDTA in Chelanox.
Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy
One of the most significant studies in this area is the Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy (TACT). This doubleblind, placebo controlled study, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, was designed to determine the safety and effectiveness of EDTA chelation therapy in individuals with coronary artery disease.
The results, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 11, showed that a course of 40 infusions of a high-dose multivitamin and disodium EDTA chelation solution modestly reduced the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including recurrent heart attacks, stroke, and death, among study participants who had previously suffered a heart attack.
Additionally, a follow-up study, TACT2 12, is currently underway to further explore the potential benefits of EDTA chelation therapy for post-heart attack patients with diabetes, as this subgroup seemed to benefit the most in the initial TACT study.
Intravenous EDTA
It’s important to note that oral chelation may not offer the same level of cardiovascular benefits as intravenous EDTA. This is because of the lower absorption rate of oral EDTA. At Bionox, we use acid resistant capsules in our chelation product to ensure better absorption of EDTA calcium. This occurs because the capsules allow it to bypass the stomach and enter the intestines for greater potential uptake. You should not use EDTA in capsule form unless it is in acid resistant capsules. Only EDTA Calcium Disodium should be used for maximum effect and safety.
Binding of Chelating Agents to Toxins
When we say chelating agents bind to toxins, we refer to a chemical process where the chelating agent forms a complex with the toxin. Chelating agents have multiple binding sites. These sites allow them to form stable complexes with metal ions. In other words, they connect with and bind to them. This ability to bind is based on the atomic structure of the chelating agent and the toxin.
Take, for example, EDTA Calcium, one of our formula’s main ingredients and a chelating agent. EDTA has a negative charge, while heavy metals like lead and mercury have a positive charge. Due to this opposite charge, the EDTA can bind to the heavy metal to form a neutral compound. This process is akin to a lock and key, where the chelating agent (the lock) fits perfectly with the metal ion (the key).
Where Do the Toxins Go?
Once the chelating agent binds to the toxin, forming a stable complex, this compound becomes water soluble and can be safely removed from the body. This process mainly occurs through renal excretion, meaning the complex is expelled in urine. Some chelating agents can also promote toxin removal through the feces.
There are several tests available to measure your body’s toxic load and determine if chelation therapy is effective:
1. **Heavy Metal Testing** This involves looking at blood, urine, or hair samples. A baseline measurement of heavy metal levels is established before starting chelation therapy. Subsequent tests are conducted to monitor any decreases in metal levels during or after the therapy.
2. **Chelation Challenge Test** This test involves taking a chelating agent and collecting 24-hour urine samples. The collected urine is then tested for heavy metals. This approach helps uncover hidden heavy metals in the body that might not be detected in standard tests.
3. **Other Laboratory Tests** Additional tests, such as a complete blood count, liver function tests, and kidney function tests, can also provide insights into the body’s capacity to manage toxins and the effectiveness of chelation therapy. These tests help identify any potential strain or damage to organs caused by heavy metals.
It’s crucial to conduct all medical procedures and tests under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider to ensure they are performed safely and accurately.
Kidney Function
Several ingredients found in modern chelation support products may have beneficial effects.
EDTA is a chelating agent known for its ability to bind to heavy metals. It can potentially aid in their removal, reducing the toxic burden on the kidneys. A study published in Biomedical Research International suggested the potential benefit of EDTA.
Chlorella Algae, known for its detoxifying properties, has also shown promise in helping renal function. Specifically, a study in the Journal of Medicinal Food suggested that Chlorella might improve renal function in dialysis patients by reducing the absorption of toxic substances in the intestines.
Modified Citrus Pectin, a specialized form of pectin, may be able to bind to and facilitate the excretion of a range of toxins, including heavy metals. This could potentially reduce the burden these toxins place on the kidneys, as highlighted in a study published in Phytotherapy Research.
Brain Detox
Several unique ingredients could support brain health and function. For instance, EDTA might reduce the harmful effects of heavy metals on the brain by helping remove them. Accumulated heavy metals are linked to neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
A review in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease pointed out the potential benefits of chelation therapy for Alzheimer’s.
Alpha Lipoic Acid, an antioxidant, has been associated with potential benefits for the brain. A review in CNS & Neurological Disorders – Drug Targets indicated that Alpha Lipoic Acid might protect the brain in conditions like multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease.
Shilajit, an ancient remedy from Ayurvedic tradition, has been credited with neuroprotective effects. A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Shilajit could enhance memory and cognitive functions in rats. This suggests it could benefit brain health.
Remember, while these findings are promising, they aren’t definitive proof of effectiveness. More studies, especially on humans, are needed to draw firm conclusions. Always check with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Liver Detox
The liver plays a key role in detoxification within the body. One of its main jobs is to filter out harmful substances from the bloodstream. When unhealthy heavy metals enter the bloodstream, it is the liver’s responsibility to help remove them, which can tax your system. Chelation therapy may support liver health by aiding in detoxification and reducing the overall toxic burden on the liver.
Here are some specifics on things that have been studied for their potential to support liver health:
- EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid). As a chelating agent, EDTA binds to heavy metals and helps remove them from the body. This can potentially reduce the strain on the liver, which otherwise would have to work harder to remove these toxins. A study published in the Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry demonstrated the ability of EDTA to chelate cadmium and reduce its toxic effects in the liver, potentially preserving liver health 13.
- Milk Thistle Seed Powder. Milk thistle is known for its liver protective properties, which can protect the liver from damage. A review published in the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine reported that silymarin, an active compound in milk thistle, can help protect the liver from toxins, including certain heavy metals 14.
- NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine). NAC is a powerful and well-known antioxidant that can help to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. A World Journal of Gastroenterology study reported that NAC may help reduce liver damage caused by various toxic substances, including heavy metals 15.
Amazing Chelation Supplements: A Preventive Measure for Health, Not a Cure for Severe Disease
Chelation therapy can often be misunderstood when taken via oral capsules. It is preventative, not a panacea or cure-all. It is not capable of curing severe diseases and chronic health conditions.
Oral chelation blends, like Chelanox, are preventive measures that aim to reduce the body’s toxic load. They help support overall health and potentially reduce the risk of specific health issues.
How They Work
Chelation works by binding to toxic metals in the body and aiding in their removal. These toxins, including heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic, can build up over time. This can be due to various factors, such as environmental pollution. Consumption of certain foods and exposure to some types of industrial work can also come into play. Over time, this toxic load can contribute to many health issues, including cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, and kidney damage. By helping to reduce this toxic load, chelation can potentially support overall health and wellness.
Ingredients in chelation products like EDTA, Chlorella Algae, and Modified Citrus Pectin have been shown in studies to bind to toxins. This potentially aids their removal from the body. This does not mean they can cure diseases caused by these toxins, but they may help reduce the risk or severity of such diseases by limiting the body’s exposure to these harmful substances.
Chelation can’t replace conventional treatments for severe diseases. Chelation supplements are not likely to reverse these conditions or act as a standalone cure for individuals with significant health conditions like late-stage cardiovascular disease, advanced kidney disease, or serious neurological disorders.
Severe diseases typically require comprehensive treatment plans overseen by healthcare professionals, including medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
Prevention
Chelating ingredients shine in preventive health care. They aid in toxin management, helping overall health and reducing disease risks. Combined with a healthy lifestyle, they form a strong disease prevention strategy. Chelation can be a valuable preventive tool, not a cure. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have health conditions or take other medications. This ensures safety and suitability.
Heavy Metals and Nitric Oxide Synthase
Introduction
Heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic, are environmental pollutants that can accumulate in the body and pose significant health risks. One of the lesser-known consequences of heavy metal exposure is the negative impact on nitric oxide synthase (NOS) production. NOS is an enzyme responsible for producing nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including vasodilation, immune response, and neurotransmission. This article will discuss the mechanisms through which heavy metals can decrease NOS production, the health implications of this reduction, and strategies to counteract these effects, with references to scientific studies supporting these claims.
Mechanisms of Heavy Metal-Induced NOS Inhibition
A. Oxidative Stress
Heavy metals can induce oxidative stress, which is characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defense mechanisms (1). Excessive ROS production can lead to the inactivation of NOS and a decrease in NO production (2). Oxidative stress also contributes to the uncoupling of endothelial NOS (eNOS), a process in which the enzyme produces superoxide instead of NO, further exacerbating the negative effects on NOS activity (3).
B. Disruption of NOS Expression and Function
Heavy metals can directly interact with NOS enzymes or alter their expression, decreasing NO production (4). For example, cadmium has been shown to inhibit NOS activity by displacing essential cofactors, such as zinc, which are necessary for proper enzyme function (5). Additionally, heavy metals can interfere with the cellular signaling pathways that regulate NOS expression, ultimately suppressing enzyme production (6).
C. Inhibition of NO Bioavailability
Heavy metals can also decrease NO bioavailability by increasing the production of molecules that scavenge and inactivate NO, such as asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) (7). ADMA, an endogenous inhibitor of NOS, competes with L-arginine, the substrate for NOS, for binding to the enzyme, thereby decreasing NO production (8).
Health Implications of Heavy Metal-Induced NOS Inhibition
A. Cardiovascular Disease
Decreased NOS activity and NO production from heavy metal exposure can impair endothelial function, reducing vasodilation and increasing blood pressure (9). This can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and hypertension (10).
B. Neurological Disorders
NO is essential for normal neurotransmission and brain function. Reduced NOS activity and NO production due to heavy metal exposure can lead to altered neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal survival, contributing to the development of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and cognitive impairment (11, 12).
C. Impaired Immune Response
NO plays a critical role in the immune response by modulating the function of immune cells and influencing cytokine production. Reduced NO production due to heavy metal-induced NOS inhibition can impair the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and maintain proper inflammatory responses (13).

Strategies to Counteract Heavy Metal-Induced NOS Inhibition
A. Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy involves the administration of chelating agents, such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) or dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), which bind to heavy metals and facilitate their excretion from the body. By reducing the body’s burden of heavy metals, chelation therapy can help restore NOS activity and improve overall health (14).
B. Antioxidant Supplementation
Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help counteract oxidative stress from heavy metals and protect NOS activity (15). Supplementation with antioxidants may help restore NO production and support overall health in individuals exposed to heavy metals.
C. Nutritional and Lifestyle Interventions
Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, essential nutrients, and anti-inflammatory compounds can help support NOS activity and counteract the effects of heavy metal exposure (16). Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining healthy body weight, and avoiding exposure to environmental pollutants can further protect NOS function and overall health.
Conclusion
Heavy metals can negatively impact nitric oxide synthase production through various mechanisms, including inducing oxidative stress, disrupting NOS expression and function, and inhibiting NO bioavailability. The detrimental effects of heavy metals on NOS activity can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and impaired immune responses. Chelation therapy, antioxidant supplementation, and nutritional and lifestyle interventions can be employed to counteract these effects. Individuals can proactively protect their health and mitigate the risks associated with heavy metal exposure by understanding the relationship between heavy metals and NOS production.
A Comprehensive Approach to Support NOS Production
This article discusses how can some components contribute to heavy metal detoxification and supports NOS production.
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is a well-known chelating agent that binds to heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, facilitating their excretion from the body (17). By removing heavy metals, EDTA can help restore NOS activity and mitigate the negative effects of these metals on nitric oxide (NO) production (18).
Modified Citrus Pectin
Modified citrus pectin is a form of pectin that has been altered to improve its bioavailability and absorption. It has been shown to bind and remove heavy metals from the body, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium (19). Modified citrus pectin can help protect NOS activity and support NO production by aiding in heavy metal detoxification.
Chlorella
Chlorella is a single-celled green alga that has been shown to possess heavy metal-binding properties, particularly for mercury (20). By assisting in removing heavy metals from the body, chlorella can help alleviate the negative effects of these metals on NOS production and support overall health.
Cilantro
Cilantro, also known as coriander, has been shown to have heavy metal-chelating properties, particularly for lead and mercury (21). By aiding in detoxifying heavy metals, cilantro can help protect NOS activity and support NO production.
Shilajit
Shilajit, a natural resinous substance found in the Himalayas, has been reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help counteract heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and inflammation (22). Shilajit can help protect NOS activity and maintain NO production by reducing oxidative stress. Additionally, shilajit has been reported to possess metal-chelating properties, which may further contribute to its heavy metal detoxification effects (23).
Zeolite
Zeolites are natural or synthetic minerals with a unique porous structure, which allows them to bind to and trap heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury (24). By assisting in removing heavy metals from the body, zeolites can help protect NOS activity and support NO production.
References:
(1) Valko, M., Morris, H., & Cronin, M. T. (2005). Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 12(10), 1161-1208. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867053764635
(2) Förstermann, U., & Sessa, W. C. (2012). Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. European Heart Journal, 33(7), 829-837. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
(3) Förstermann, U., & Münzel, T. (2006). Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace. Circulation, 113(13), 1708-1714. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602532
(4) Brüne, B., Schmidt, K. U., & Ullrich, V. (1990). Activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by carbon monoxide and inhibition by superoxide anion. European Journal of Biochemistry, 192(2), 683-688. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19283.x
(5) Ercal, N., Gurer-Orhan, H., & Aykin-Burns, N. (2001). Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 1(6), 529-539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831
(6) Pacher, P., Beckman, J. S., & Liaudet, L. (2007). Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiological Reviews, 87(1), 315-424. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2006
(7) Kielstein, J. T., & Cooke, J. P. (2005). Cardiology and nephrology converge on a common problem: asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, predicts cardiovascular events. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 16(9), 2454-2457. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005060610
(8) Böger, R. H. (2006). Asymmetric dimethylarginine, an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, explains the “L-arginine paradox” and acts as a novel cardiovascular risk factor. Journal of Nutrition, 136(10), 2882S-2887S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.10.2882S
(9) Vaziri, N. D. (2008). Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 295(2), H454-H465. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00158.2008
(10) Navas-Acien, A., Guallar, E., Silbergeld, E. K., & Rothenberg, S. J. (2007). Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115(3), 472-482. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9785
(11) Farina, M., Avila, D. S., da Rocha, J. B., & Aschner, M. (2013). Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: a focus on iron, manganese and mercury. Neurochemistry International, 62(5), 575-594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.12.006
(12) Sanders, T., Liu, Y., Buchner, V., & Tchounwou, P. B. (2009). Neurotoxic effects and biomarkers of lead exposure: a review. Reviews on Environmental Health, 24(1), 15-45. https://doi.org/10.151 5/reveh.2009.24.1.15
(13) Bogdan, C. (2001). Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nature Immunology, 2(10), 907-916. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1001-907
(14) Flora, S. J., & Pachauri, V. (2010). Chelation in metal intoxication. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(7), 2745-2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7072745
(15) Lobo, V., Patil, A., Phatak, A., & Chandra, N. (2010). Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 4(8), 118-126. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.70902
(16) Crinnion, W. J. (2010). The role of nutritional supplements in the treatment of heavy metal toxicity. Alternative Medicine Review, 15(1), 33-47. http://archive.foundationalmedicinereview.com/publications/15/1/33.pdf
(17) Flora, S. J., & Pachauri, V. (2010). Chelation in metal intoxication. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(7), 2745-2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7072745
(18) Vaziri, N. D. (2008). Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 295(2), H454-H465. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00158.2008
(19) Eliaz, I., Weil, E., & Wilk, B. (2019). Integrative medicine and the role of modified citrus pectin/alginates in heavy metal chelation and detoxification – five case reports. Functional Foods in Health and Disease, 8(12), 430-443. https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v8i12.569
(20) Uchikawa, T., Yasutake, A., Kumamoto, Y., Maruyama, I., Kumamoto, S., & Ando, Y. (2011). The influence of Parachlorella beyerinckii CK-5 on the absorption and excretion of methylmercury (MeHg) in mice. Journal of Toxicological Sciences, 36(1), 121-130. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.36.121
(21) Aga, M., Iwaki, K., Ueda, Y., Ushio, S., Masaki, N., Fukuda, S., … & Ito, Y. (2001). Preventive effect of Coriandrum sativum (Chinese parsley) on localized lead deposition in ICR mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 77(2-3), 203-208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(01)00289-X
(22) Carrasco-Gallardo, C., Guzmán, L., & Maccioni, R. B. (2012). Shilajit: a natural phytocomplex with potential procognitive activity. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2012, 674142. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/674142
(23) Bhattacharyya, S., & Pal, D. (2013). In vitro study of the effects of Shilajit on the activities of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Pharmaceutical Biology, 51(2), 269-272. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2012.727360
(24) Selvam, T., Schwieger, W., & Dathe, W. (2017). The potential of natural and modified zeolites for heavy metal capture in contaminated waters. In Natural Mineral Nanotubes (pp. 363-380). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/b18522-16