Stop Taking Arginine you say? Is there a reason you should stop or is there simply a better way to take it? Lets see!
Scientists discovered arginine, an amino acid, in the late 19th century. Its use has surged in popularity over the years as a coveted supplement among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. It is also popular amoung those seeking to improve their cardiovascular health. Also, it can support lower blood pressure and offers support for those seeking cognitive improvements.
What Is Arginine?
This semi-essential amino acid plays a pivotal role in synthesizing proteins and supporting nitric oxide production in the body. It also enhances blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscle tissues. Its reputation for boosting exercise performance, aiding in recovery, and offering cardiovascular benefits is well know. This reputation has cemented arginine’s place on the shelves of health stores and in the regimens of health-conscious individuals worldwide. But does it work? Should you stop taking arginine?
The burgeoning interest in arginine has also ushered in a wave of scrutiny and research aimed at understanding its efficacy.
Arginine’s Benefits
Arginine’s benefits are not in dispute. Emerging evidence, however, suggests that its effectiveness can be significantly amplified when combined with other nutrients. So and we aim to show why your should stop taking arginine alone. This article aims to shed light on the limitations of solo arginine supplementation. We strongly advocate for its combination with other nutrients because of improved health outcomes.
One of the primary reasons behind the push for combining arginine with other ingredients lies in its bioavailability. The body’s ability to utilize it effectively is a common concern. It also has a powerful effect of other substances such as NOS ( Nitric Oxide Synthase). When taken alone, the absorption of arginine can encounter physiological barriers that limit its effectiveness, absorption and lifespan.
Other Amino Acids
The presence of other amino acids can compete with arginine for absorption in the gut. This reduces the amount that ultimately enters the bloodstream and reaches the tissues where it is most needed. However, some amino acids have the opposite effect and can boost its effect! Just this alone is a great justification for why you should stop taking arginine alone!
This competition from the wrong kinds of amino acids can diminish the perceived benefits of arginine. This is particularly so in the realms of exercise performance and cardiovascular health.
Better Blood Vessel Dilation
Arginine’s role in the production of nitric oxide has been well-documented. This is because the conversion of arginine into nitric oxide can be inefficient without other complementary nutrients. This inefficiency highlights another limitation of relying solely on arginine. To achieve desired health outcomes, such as improved blood flow and improved exercise capacity, more is needed.
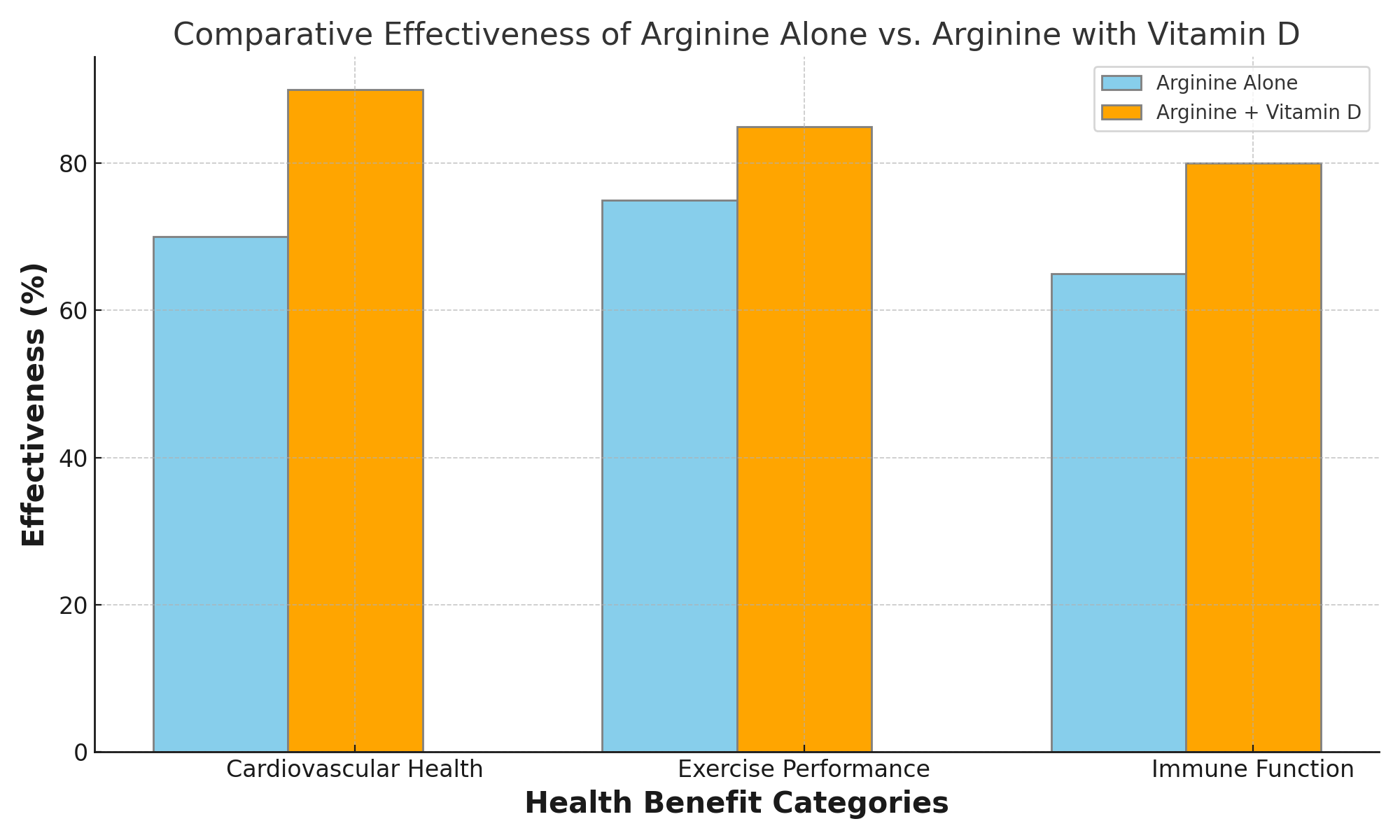
The case for combining arginine with other nutrients also extends to its synergistic interactions with certain vitamins and minerals. For example, vitamin D has been shown to work in tandem with arginine to bolster the immune system. It also plays a role in helping to support bone health. Antioxidants like vitamins E and C can enhance arginine’s cardiovascular benefits by reducing stress and inflammation. These interactions underscore the multifaceted nature of nutrition and wellness. This is because the combined effect of different nutrients often surpasses the sum of their individual benefits.
Arginine As A Supplement
The purpose of this article is not to diminish the value of arginine as a supplement. We aim to illuminate a more nature based approach to its use. By combining arginine with complementary nutrients such as citrulline, vitamin D, horse chestnut, and vitamins E and C, individuals can potentially unlock a broader spectrum of health benefits and achieve more pronounced improvements in cardiovascular health, exercise performance, and overall well-being.
As we delve deeper into the limitations of solo arginine supplementation it becomes clear that the path to optimal health is not through isolated ingredients. We see it is through a well-rounded and informed approach to nutrition. This perspective enriches our understanding of how different nutrients interact. It also empowers us to make more effective decisions about our health and wellness strategies.
Reason 1: Limited Absorption and Bioavailability
Arginine, when consumed as a standalone supplement, faces significant challenges related to its absorption and bioavailability in the human body. This amino acid competes with other amino acids for transporters in the gut and bloodstream. This competition can significantly reduce the amount of arginine that is effectively absorbed and utilized by the body. Yet another reason why you should stop taking arginine alone.
Absorption
The presence of other amino acids in the digestive system can inhibit arginine’s entry into the bloodstream. This sometimes diminishes its overall effectiveness, making it a waste of time and money to consume.
The bioavailability of arginine is not just about how much is absorbed. How efficiently it is used by the body is also important. This is because once absorbed, arginine serves as a precursor for the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO). As mentioned before NO a critical molecule for cardiovascular health, immune function, and wound healing.
The conversion rate of arginine to nitric oxide can be lowered or just plan stopped in the absence of complementary nutrients. This leads to less than ideal health outcomes. So to summarize, add the wrong things and arginine may not work. Add the right things and you can put it in overdrive!
Combinations That Count: Stop Taking Arginine By Itself
The issue of limited absorption and bioavailability underscores the importance of not just consuming arginine but ensuring it is taken correctly. This can be improved by combining arginine with other things that enhance its absorption or work together to bolster its effects.
For instance, pairing arginine with citrulline, another amino acid, has been shown to enhance the overall bioavailability of arginine, see chart below for more info.
Citrulline is converted into arginine in the kidney, which not only increases the plasma levels of arginine but also prolongs its availability for nitric oxide production, thereby amplifying the cardiovascular benefits.
Summary of Reason #1
So in summary, while arginine alone possesses undeniable health benefits, its limited absorption and bioavailability can hinder its effectiveness. There are great reasons why you may want to stop taking arginine alone. By understanding and addressing these limitations through strategic supplementation, individuals can better harness arginine’s potential health benefits. This approach not only optimizes the intake of arginine but also underscores a broader principle. That being; nutritional supplementation often yields the best results when approached naturally.
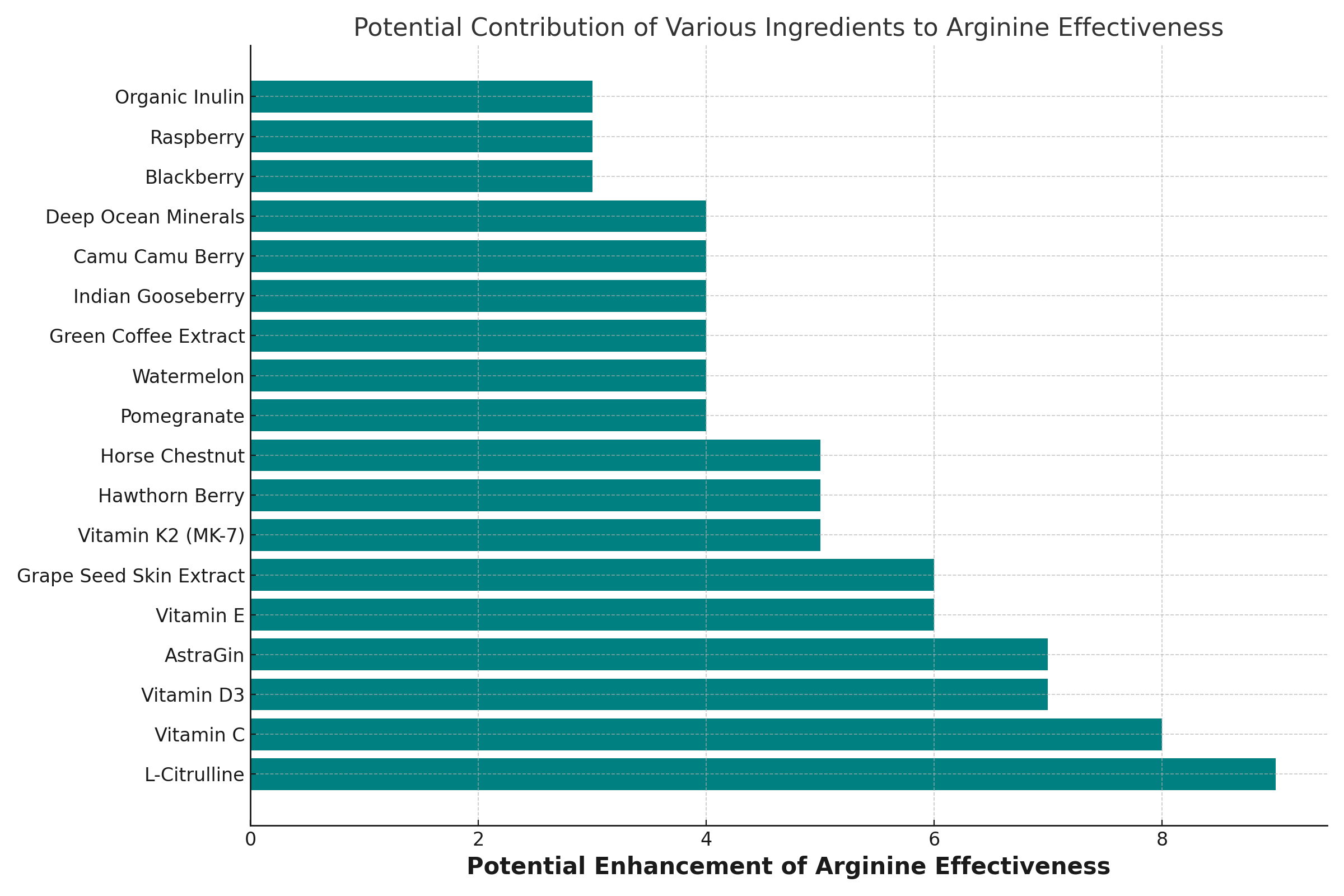
Stop Taking Arginine Alone
- Vitamin C: Enhances nitric oxide production from Arginine by stabilizing it and reducing its breakdown.
- Vitamin D3: Works synergistically to support cardiovascular health and may enhance the effectiveness of Arginine. Vitamin D also helps your body produce more NOS.
- Vitamin E: Protects cells from cellular stress, potentially enhancing Arginine’s effects on vascular health.
- Vitamin K2 (MK-7): May work with Arginine to support arterial health and flexibility.
- L-Citrulline: Converts to Arginine in the body, increasing Arginine levels and nitric oxide production.
- Pomegranate, Watermelon, Blackberry, Raspberry: These fruits are rich in antioxidants and other compounds that can support nitric oxide production and enhance the effects of Arginine.
- Hawthorn Berry, Horse Chestnut: Known for their vascular health benefits, potentially complementing Arginine’s cardiovascular effects.
- Green Coffee Extract, Indian Gooseberry, Grape Seed Skin Extract, Camu Camu Berry: These ingredients offer antioxidant support, which can synergize with Arginine’s health benefits.
- Deep Ocean Minerals: May provide trace minerals that support overall metabolic processes, including those involving Arginine.
- AstraGin: Known to enhance nutrient absorption, potentially improving Arginine bioavailability.
- Organic Inulin: A prebiotic fiber that can support gut health, possibly affecting Arginine’s absorption positively.
Cardiovascular Health
Arginine is well-known for its critical role in the production of nitric oxide (NO). NO is a vital molecule that influences various aspects of cardiovascular health as we have discussed above.
Nitric oxide acts as a vasodilator, meaning it relaxes the inner muscles of blood vessels. This causes them to widen and thereby improve blood flow and energy, etc.
This effect can lower blood pressure, enhance exercise performance, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It even helps with some cognitive issues and diseases of the eye as well.
Despite its potential, the production of nitric oxide from arginine can be hampered when arginine is consumed alone. This is due to factors like enzyme availability, oxidative stress, and the presence of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA). ADMA is a natural inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis. In other words, if you stop taking arginine by itself, you get more of it. The results are better if your taking it with the right things.
Citrulline
The combination of arginine with citrulline is a strategy that can overcome these limitations. Combining the two can lead to more efficient nitric oxide production. This is yet another reason why you may want to top taking arginine alone. Citrulline is converted into arginine in the kidneys. It increases the plasma levels of arginine and also provides a more sustained release of arginine for nitric oxide production. Combining bypasses the competitive absorption issues in the gut. It also helps maintain higher levels of nitric oxide in the bloodstream. Combining the two enhanci cardiovascular benefits such as improved vascular tone, blood flow, and reduced blood pressure.
Vitamins E, C, and K2
These play supportive roles in enhancing nitric oxide production and ensuring its stability:
Vitamin E
This antioxidant helps protect nitric oxide from degradation via oxidatiion that can rapidly neutralize nitric oxide. It reduces the availability and effectiveness of NO in vasodilation. By reducing oxidative stress, vitamin E preserves nitric oxide levels. More NO means more cardiovascular benefits.

Vitamin C
Similar to vitamin E, vitamin C is an antioxidant that can synergize with arginine by stabilizing nitric oxide. Vitamin C reduces its breakdown in the bloodstream. C has also been shown to regenerate vitamin E, thus working together. These vitamins create a powerful antioxidant network that protects nitric oxide and enhances its effects on blood vessel dilation.

Vitamin K2 (MK-7)
While its role in nitric oxide production may not be as apparent as other vitamins, vitamin K2 contributes to cardiovascular health. It does so by preventing calcium deposition in the arteries. This action helps maintain arterial flexibility and function. There is emerging evidence that vitamin K2 may also support the endothelial function. This is is crucial for nitric oxide production and regulation. By promoting overall vascular health, vitamin K2 can indirectly support the optimal function of nitric oxide.

So, while arginine is a key precursor to nitric oxide its solo use can result in poor nitric oxide production. This is due to various physiological constraints, making it kind of a waste of money to take alone.
Combining arginine with citrulline and other vitamins can significantly enhance the production of nitric oxide. This strategic supplementation approach not only amplifies the cardiovascular benefits. It also supports broader health outcomes and benefits. This is done by ensuring efficient blood flow and nutrient delivery throughout the body and therefore more nitric oxide.
Reason 3: Inadequate Support for Vascular Health
Vascular health is fundamental to the overall well-being of the cardiovascular system, brain, gut, you name it. Healthy blood vessels are essential for the efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients to every part of the body. They also are vital for the removal of waste products, energy, vitality and pretty much everything.
Good vascular health also plays a critical role in preventing conditions such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and PAD to name a few. While arginine is renowned for its capacity to enhance nitric oxide production and thus improve vasodilation and blood flow, relying on arginine alone might not offer comprehensive support for vascular health. This is because vascular health encompasses more than just the ability of blood vessels to dilate; it also includes the strength, elasticity, and integrity of the blood vessel walls.
Horse Chestnut
Enter the synergistic potential of combining arginine with horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum), an herbal supplement known for its heart healthy properties. Horse chestnut can significantly enhance heart health. This amazing plant contains a compound called aescin. The active ingredients in aescin have been shown to strengthen capillary walls, reduce inflammation, and improve blood vessel tone. This can be particularly beneficial in conditions such as chronic venous insufficiency, where veins struggle to return blood to the heart efficiently.

The combination of arginine and horse chestnut works on multiple fronts to support vascular health. This is because of arginine’s role in nitric oxide production addresses the need for vasodilation and improved blood flow. Horse chestnut’s heart healthy and anti-inflammatory effects contribute to the structural health and functionality of the blood vessels.
Dual Action
This dual-action approach ensures that blood vessels are not only capable of adjusting their diameter for optimal blood flow but are also strong, resilient, and less prone to damage and inflammation.
Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of horse chestnut complement arginine’s cardiovascular benefits by protecting the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels. This protection can lead to stopping endothelial dysfunction, a precursor to atherosclerosis and other circulatory diseases. By stopping oxidative damage, the combination of arginine and horse chestnut supports the integrity of the inner veins, enhancing its capacity to produce nitric oxide and maintain vascular health.
In summary, while arginine alone offers significant benefits for enhancing nitric oxide production and improving vasodilation, it may not provide complete support for the multifaceted aspects of vascular health. Incorporating horse chestnut into a supplementation regimen that includes arginine can offer a more basic approach to maintaining and improving vascular health. This combination not only optimizes blood flow but also addresses the structural and functional needs of blood vessels, offering a comprehensive strategy for cardiovascular wellness.
Reason 4: Better Nitric Oxide Production with Vitamin D Supplementation: Stop Taking Arginine Alone
Vitamin D’s relationship with arginine extends beyond basic nutritional synergy, directly impacting the efficiency of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), the enzyme responsible for NO production from arginine. This interaction is crucial for understanding how the combination of arginine and vitamin D can significantly amplify and promote cardiovascular health, immune function, and overall well-being.
Vitamin D has been shown to enhance the expression and activity of nitric oxide synthase, thereby increasing the conversion of arginine into nitric oxide and this increase in nitric oxide availability is vital for vasodilation, which improves blood flow and reduces blood pressure, supporting your heart.
More NO
The enhancement of NO production by vitamin D not only increases the heart health benefits provided by arginine but also supports the function of the inner lining of blood vessels, further protecting against arterial stiffness and cardiovascular disease.
The synergy between vitamin D and arginine in creating higher nitric oxide levels has broader health implications as well, especially for your immune system and bone health. Elevated NO levels can improve immune response by supporting the body’s defense mechanisms against diseases. Nitric oxide acts as a signaling molecule in the immune system, managing various processes involved in the immune response. Vitamin D, well-recognized for its role in supporting immune function and reducing inflammation, works in concert with arginine-derived NO to create a more effective immune response.
In terms of bone health, the improved blood flow resulting from increased nitric oxide production ensures that nutrients essential for bone maintenance, including calcium and phosphate, are efficiently delivered and utilized in the body.
Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D plays a direct role in calcium absorption and bone mineralization, making its combination with arginine a strategic approach to supporting skeletal health and heart health.
Arguing for the effectiveness of taking arginine with vitamin D rests on understanding these mechanisms as well as vitamin D’s ability to increase nitric oxide synthase and increase nitric oxide production from arginine. This provides a compelling reason to combine Vit D for improved health outcomes. This synergy not only enhances cardiovascular benefits by improving vascular function and reducing blood pressure but also supports robust immune function and contributes to the maintenance of healthy bones.
The combination of arginine and vitamin D offers a potent approach to health supplementation, with vitamin D significantly enhancing the conversion of arginine into nitric oxide and thereby amplifying the benefits of arginine supplementation. This partnership between vitamin D and arginine underscores the importance of a natural approach to supplementation, where the combined effects of nutrients are leveraged to achieve the best health outcomes.
Reason 5: Reduced Antioxidant Protection
Antioxidants play a pivotal role in safeguarding the body against oxidation, a condition characterized by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage your cells, contributing to aging and various diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer, obviously things no one wants!
Antioxidants neutralize these nasty free radicals, thus protecting the body from damage. While arginine is known for its cardiovascular and immune system benefits, its antioxidant potential can be significantly improved when combined with vitamins E and C, both of which are powerful antioxidants. Also antioxidants make the nitric oxide molecule last longer, so they boost nitric oxides lifespan, and therefore effect! Yet another good reason you want to stop taking arginine by itself!
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that protects cell membranes from cellular damage by reacting with free radicals, which prevents the propagation of free radical damage within the body. This vitamin is particularly effective in protecting against lipid peroxidation, a process that can compromise cell membrane integrity and function. By maintaining cell membrane health, vitamin E supports the optimal functioning of cells, including those involved in the synthesis and utilization of arginine.
Vitamin C, a water-soluble antioxidant, complements vitamin E by neutralizing free radicals in the aqueous environments of the body. Furthermore, vitamin C can regenerate oxidized vitamin E, thereby restoring its antioxidant capacity making this a synergistic interaction that enhances the body’s overall antioxidant defense system.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C also plays a crucial role in the synthesis of collagen, a protein essential for the maintenance of blood vessels, skin, and connective tissues. The presence of adequate vitamin C can thus support the structural health of blood vessels, ensuring a conducive environment for arginine’s cardiovascular benefits.
The combination of arginine with vitamins E and C offers a multi-faceted approach to combating oxidative stress and supporting your health. Arginine, through its role in nitric oxide production, can improve vascular health and support the delivery of nutrients, including antioxidants, to tissues throughout the body while, vitamins E and C directly neutralize free radicals and protect against cellular damage. This collective action increases the antioxidant potential of these nutrients and also enhances their individual benefits. These benefits being mostly related to cardiovascular health, immune function, and tissue repair.
Advocating for the combination of arginine with vitamins E and C is grounded in the understanding that optimal personal health outcomes are often achieved through synergistic nutritional strategies.
This approach leverages the complementary actions of arginine and antioxidants to fortify the body’s defenses against disease, thereby supporting overall health and well-being.
By incorporating these nutrients into a comprehensive supplementation regimen, you can harness a more potent antioxidant defense, offering broader protection against damage and its associated health risks.

