Boosting NOS Production a Guide
Introduction
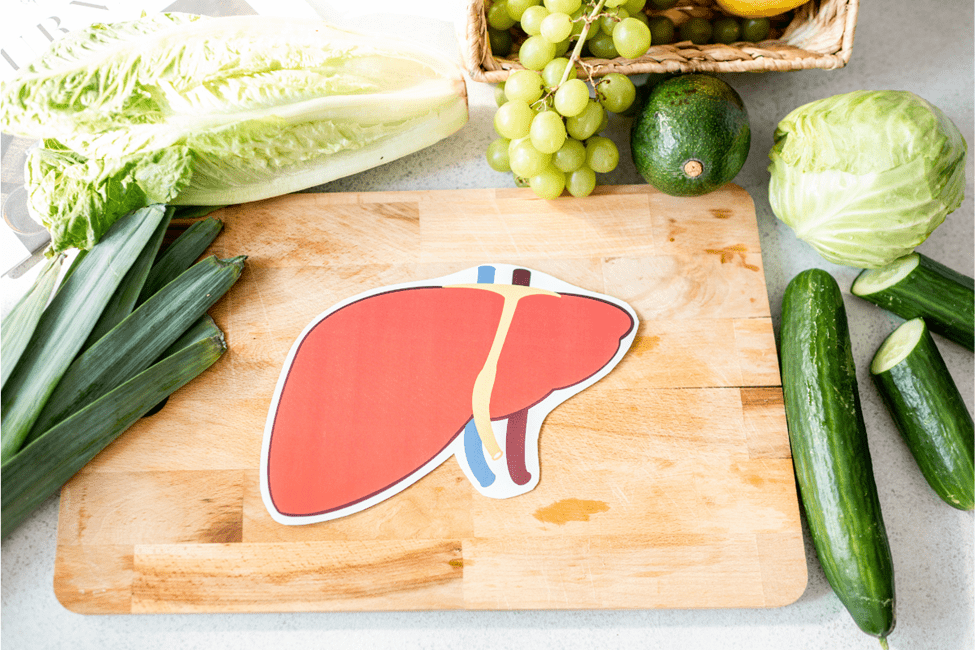
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) is an enzyme responsible for producing nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including vasodilation, immune response, and neurotransmission. Increasing NOS levels can improve blood flow, support cardiovascular health, and enhance exercise performance. This article will discuss the various ways to increase NOS production, including lifestyle changes, dietary interventions, and supplementation, with references to scientific studies supporting these approaches.
Lifestyle Changes
A. Exercise
Regular physical activity has been shown to increase NOS production by promoting the expression and activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) (1). Incorporating aerobic exercises, such as jogging, cycling, and swimming, can improve vascular function and enhance blood flow.
B. Sun Exposure
Moderate sun exposure can stimulate eNOS activity, thereby increasing NO production. Ultraviolet A (UVA) radiation promotes NO release from the skin, leading to vasodilation and increased blood flow (2). Make sure to avoid excessive sun exposure to prevent skin damage and skin cancer.
Dietary Interventions
A. Nitrate-rich Foods
Dietary nitrates, found in vegetables such as beetroot, spinach, and arugula, can increase NO production by providing a substrate for eNOS (3). Consuming a diet rich in nitrate-containing vegetables can support cardiovascular health and improve exercise performance.
B. Antioxidant-rich Foods
Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, dark chocolate, and green tea, can promote eNOS activity by reducing oxidative stress (4). Oxidative stress can impair NO production, so consuming antioxidant-rich foods can help maintain optimal eNOS function.
Supplementation
A. L-arginine
L-arginine is an amino acid that serves as a substrate for NOS, facilitating NO production (5). Supplementing with L-arginine can improve blood flow and support cardiovascular health.
B. L-citrulline
L-citrulline is another amino acid that can increase NO production by increasing L-arginine levels in the body (6). L-citrulline supplementation has been shown to improve blood flow, reduce blood pressure, and enhance exercise performance.
C. Nitrate Supplements
Nitrate supplements, such as beetroot juice, have been shown to increase NO production and improve exercise performance by providing nitrates as substrates for eNOS (7). Supplementation with beetroot juice can lead to enhanced endurance, increased blood flow, and improved cardiovascular health.
D. Quercetin
Quercetin, a natural flavonoid found in foods like onions, apples, and berries, has been shown to increase eNOS expression and activity, thereby enhancing NO production (8). Supplementation with quercetin can support cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation.
E. Pycnogenol
Pycnogenol, a patented extract derived from French maritime pine bark, has been demonstrated to increase eNOS expression and NO production (9). Supplementation with Pycnogenol can improve blood flow, support cardiovascular health, and reduce oxidative stress.

Conclusion
Increasing nitric oxide synthase production in the body can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary interventions, and supplementation. Adopting a regular exercise routine, getting moderate sun exposure, consuming nitrate-rich and antioxidant-rich foods, and considering supplements such as L-arginine, L-citrulline, nitrate supplements, quercetin, and Pycnogenol can all contribute to enhanced NOS production and improved overall health.
It is important to note that individual responses to these interventions may vary, and it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your lifestyle or incorporating new supplements into your routine. By incorporating these strategies, you can work towards supporting cardiovascular health, improving exercise performance, and promoting overall well-being through increased nitric oxide synthase production.
Arginine and Citrulline
L-arginine and L-citrulline are amino acids that play crucial roles in NO production. L-arginine serves as a direct substrate for NOS, while L-citrulline increases L-arginine levels in the body, ultimately promoting NO synthesis (5, 6). Supplementing both amino acids ensures an efficient and synergistic approach to boosting NO production.
Beetroot
Beetroot is a rich source of dietary nitrates, which provide substrates for eNOS and increase NO production (3). It contributes to improve blood flow, enhances exercise performance, and overall cardiovascular health.
Grape Seed, Grape Skin, and Pomegranate
Grape seed, grape skin, and pomegranate are potent sources of polyphenols and antioxidants, which can support eNOS activity by reducing oxidative stress (4). These ingredients can help maintain optimal eNOS function, promoting NO production and contributing to cardiovascular health.
Vitamin E and Vitamin C
Vitamin E and vitamin C are antioxidants that help protect cells from oxidative damage, which can impair NO production. (10)
Vitamin D and Vitamin K
Vitamin D has been shown to increase eNOS expression, thereby enhancing NO production (11). Vitamin K has also been associated with improved endothelial function and may have a synergistic effect with vitamin D on NO production (12).
References:
(1) Green, D. J., Maiorana, A., O'Driscoll, G., & Taylor, R. (2004). Effect of exercise training on endothelium‐derived nitric oxide function in humans. The Journal of physiology, 561(1), 1-25. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.068197
(2) Liu, D., Fernandez, B. O., Hamilton, A., Lang, N. N., Gallagher, J. M., Newby, D. E., ... & Feelisch, M. (2014). UVA irradiation of human skin vasodilates arterial vasculature and lowers blood pressure independently of nitric oxide synthase. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 134(7), 1839-1846. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2014.27
(3) Hord, N. G., Tang, Y., & Bryan, N. S. (2009). Food sources of nitrates and nitrites: the physiologic context for potential health benefits. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 90(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.27131
(4) Förstermann, U., & Li, H. (2011). Therapeutic effect of enhancing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression and preventing eNOS uncoupling. British journal of pharmacology, 164(2), 213-223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01395.x
(5) Böger, R. H. (2004). The pharmacodynamics of L-arginine. Journal of Nutrition, 134(10), 2807S-2811S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/134.10.2807S
(6) Bailey, S. J., Blackwell, J. R., Lord, T., Vanhatalo, A., Winyard, P. G., & Jones, A. M. (2015). L-citrulline supplementation improves O2 uptake kinetics and high-intensity exercise performance in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology, 119(4), 385-395. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00192.2014
(7) Jones, A. M., Thompson, C., Wylie, L. J., & Vanhatalo, A. (2018). Dietary nitrate and physical performance. Annual review of nutrition, 38, 303-328. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-082117-051622
(8) Larson, A. J., Symons, J. D., & Jalili, T. (2012). Therapeutic potential of quercetin to decrease blood pressure: a review of efficacy and mechanisms. Advances in Nutrition, 3(1), 39-46. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.111.001271
(9) Enseleit, F., Sudano, I., Périat, D., Winnik, S., Wolfrum, M., Flammer, A. J., ... & Lüscher, T. F. (2012). Effects of Pycnogenol on endothelial function in patients with stable coronary artery disease: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. European Heart Journal, 33(13), 1589-1597. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr482
(10) Tousoulis, D., Kampoli, A. M., Tentolouris, C., Papageorgiou, N., & Stefanadis, C. (2012). The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function. Current Vascular Pharmacology, 10(1), 4-18. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016112798829760
(11) Andrukhova, O., Slavic, S., Zeitz, U., Riesen, S. C., Heppelmann, M. S., Ambrisko, T. D., ... & Erben, R. G. (2014). Vitamin D is a regulator of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and arterial stiffness in mice. Molecular Endocrinology, 28(1), 53-64. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2013-1252
(12) Vossen, L. M., Schurgers, L. J., van Varik, B. J., Kietselaer, B. L., Vermeer, C., Meeder, J. G., ... & de Leeuw, P. W. (2015). Menaquinone-7 supplementation to reduce vascular calcification in patients with coronary artery disease: rationale and study protocol (VitaK-CAC Trial). Nutrients, 7(10), 8905-8915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7105423
Heavy Metals and Nitric Oxide Synthase
Introduction
Heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic, are environmental pollutants that can accumulate in the body and pose significant health risks. One of the lesser-known consequences of heavy metal exposure is the negative impact on nitric oxide synthase (NOS) production. NOS is an enzyme responsible for producing nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including vasodilation, immune response, and neurotransmission. This article will discuss the mechanisms through which heavy metals can decrease NOS production, the health implications of this reduction, and strategies to counteract these effects, with references to scientific studies supporting these claims.
Mechanisms of Heavy Metal-Induced NOS Inhibition
A. Oxidative Stress
Heavy metals can induce oxidative stress, which is characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defense mechanisms (1). Excessive ROS production can lead to the inactivation of NOS and a decrease in NO production (2). Oxidative stress also contributes to the uncoupling of endothelial NOS (eNOS), a process in which the enzyme produces superoxide instead of NO, further exacerbating the negative effects on NOS activity (3).
B. Disruption of NOS Expression and Function
Heavy metals can directly interact with NOS enzymes or alter their expression, decreasing NO production (4). For example, cadmium has been shown to inhibit NOS activity by displacing essential cofactors, such as zinc, which are necessary for proper enzyme function (5). Additionally, heavy metals can interfere with the cellular signaling pathways that regulate NOS expression, ultimately suppressing enzyme production (6).
C. Inhibition of NO Bioavailability
Heavy metals can also decrease NO bioavailability by increasing the production of molecules that scavenge and inactivate NO, such as asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) (7). ADMA, an endogenous inhibitor of NOS, competes with L-arginine, the substrate for NOS, for binding to the enzyme, thereby decreasing NO production (8).
Health Implications of Heavy Metal-Induced NOS Inhibition
A. Cardiovascular Disease
Decreased NOS activity and NO production from heavy metal exposure can impair endothelial function, reducing vasodilation and increasing blood pressure (9). This can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and hypertension (10).
B. Neurological Disorders
NO is essential for normal neurotransmission and brain function. Reduced NOS activity and NO production due to heavy metal exposure can lead to altered neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal survival, contributing to the development of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and cognitive impairment (11, 12).
C. Impaired Immune Response
NO plays a critical role in the immune response by modulating the function of immune cells and influencing cytokine production. Reduced NO production due to heavy metal-induced NOS inhibition can impair the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and maintain proper inflammatory responses (13).

Strategies to Counteract Heavy Metal-Induced NOS Inhibition
A. Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy involves the administration of chelating agents, such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) or dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), which bind to heavy metals and facilitate their excretion from the body. By reducing the body’s burden of heavy metals, chelation therapy can help restore NOS activity and improve overall health (14).
B. Antioxidant Supplementation
Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help counteract oxidative stress from heavy metals and protect NOS activity (15). Supplementation with antioxidants may help restore NO production and support overall health in individuals exposed to heavy metals.
C. Nutritional and Lifestyle Interventions
Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, essential nutrients, and anti-inflammatory compounds can help support NOS activity and counteract the effects of heavy metal exposure (16). Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining healthy body weight, and avoiding exposure to environmental pollutants can further protect NOS function and overall health.
Conclusion
Heavy metals can negatively impact nitric oxide synthase production through various mechanisms, including inducing oxidative stress, disrupting NOS expression and function, and inhibiting NO bioavailability. The detrimental effects of heavy metals on NOS activity can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and impaired immune responses. Chelation therapy, antioxidant supplementation, and nutritional and lifestyle interventions can be employed to counteract these effects. Individuals can proactively protect their health and mitigate the risks associated with heavy metal exposure by understanding the relationship between heavy metals and NOS production.
A Comprehensive Approach to Support NOS Production
This article discusses how can some components contribute to heavy metal detoxification and supports NOS production.
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is a well-known chelating agent that binds to heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, facilitating their excretion from the body (17). By removing heavy metals, EDTA can help restore NOS activity and mitigate the negative effects of these metals on nitric oxide (NO) production (18).
Modified Citrus Pectin
Modified citrus pectin is a form of pectin that has been altered to improve its bioavailability and absorption. It has been shown to bind and remove heavy metals from the body, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium (19). Modified citrus pectin can help protect NOS activity and support NO production by aiding in heavy metal detoxification.
Chlorella
Chlorella is a single-celled green alga that has been shown to possess heavy metal-binding properties, particularly for mercury (20). By assisting in removing heavy metals from the body, chlorella can help alleviate the negative effects of these metals on NOS production and support overall health.
Cilantro
Cilantro, also known as coriander, has been shown to have heavy metal-chelating properties, particularly for lead and mercury (21). By aiding in detoxifying heavy metals, cilantro can help protect NOS activity and support NO production.
Shilajit
Shilajit, a natural resinous substance found in the Himalayas, has been reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help counteract heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and inflammation (22). Shilajit can help protect NOS activity and maintain NO production by reducing oxidative stress. Additionally, shilajit has been reported to possess metal-chelating properties, which may further contribute to its heavy metal detoxification effects (23).
Zeolite
Zeolites are natural or synthetic minerals with a unique porous structure, which allows them to bind to and trap heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury (24). By assisting in removing heavy metals from the body, zeolites can help protect NOS activity and support NO production.
References:
(1) Valko, M., Morris, H., & Cronin, M. T. (2005). Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 12(10), 1161-1208. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867053764635
(2) Förstermann, U., & Sessa, W. C. (2012). Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. European Heart Journal, 33(7), 829-837. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
(3) Förstermann, U., & Münzel, T. (2006). Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace. Circulation, 113(13), 1708-1714. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602532
(4) Brüne, B., Schmidt, K. U., & Ullrich, V. (1990). Activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by carbon monoxide and inhibition by superoxide anion. European Journal of Biochemistry, 192(2), 683-688. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19283.x
(5) Ercal, N., Gurer-Orhan, H., & Aykin-Burns, N. (2001). Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 1(6), 529-539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831
(6) Pacher, P., Beckman, J. S., & Liaudet, L. (2007). Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiological Reviews, 87(1), 315-424. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2006
(7) Kielstein, J. T., & Cooke, J. P. (2005). Cardiology and nephrology converge on a common problem: asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, predicts cardiovascular events. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 16(9), 2454-2457. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005060610
(8) Böger, R. H. (2006). Asymmetric dimethylarginine, an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, explains the “L-arginine paradox” and acts as a novel cardiovascular risk factor. Journal of Nutrition, 136(10), 2882S-2887S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.10.2882S
(9) Vaziri, N. D. (2008). Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 295(2), H454-H465. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00158.2008
(10) Navas-Acien, A., Guallar, E., Silbergeld, E. K., & Rothenberg, S. J. (2007). Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115(3), 472-482. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9785
(11) Farina, M., Avila, D. S., da Rocha, J. B., & Aschner, M. (2013). Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: a focus on iron, manganese and mercury. Neurochemistry International, 62(5), 575-594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.12.006
(12) Sanders, T., Liu, Y., Buchner, V., & Tchounwou, P. B. (2009). Neurotoxic effects and biomarkers of lead exposure: a review. Reviews on Environmental Health, 24(1), 15-45. https://doi.org/10.151 5/reveh.2009.24.1.15
(13) Bogdan, C. (2001). Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nature Immunology, 2(10), 907-916. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1001-907
(14) Flora, S. J., & Pachauri, V. (2010). Chelation in metal intoxication. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(7), 2745-2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7072745
(15) Lobo, V., Patil, A., Phatak, A., & Chandra, N. (2010). Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 4(8), 118-126. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.70902
(16) Crinnion, W. J. (2010). The role of nutritional supplements in the treatment of heavy metal toxicity. Alternative Medicine Review, 15(1), 33-47. http://archive.foundationalmedicinereview.com/publications/15/1/33.pdf
(17) Flora, S. J., & Pachauri, V. (2010). Chelation in metal intoxication. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(7), 2745-2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7072745
(18) Vaziri, N. D. (2008). Mechanisms of lead-induced hypertension and cardiovascular disease. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 295(2), H454-H465. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00158.2008
(19) Eliaz, I., Weil, E., & Wilk, B. (2019). Integrative medicine and the role of modified citrus pectin/alginates in heavy metal chelation and detoxification – five case reports. Functional Foods in Health and Disease, 8(12), 430-443. https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v8i12.569
(20) Uchikawa, T., Yasutake, A., Kumamoto, Y., Maruyama, I., Kumamoto, S., & Ando, Y. (2011). The influence of Parachlorella beyerinckii CK-5 on the absorption and excretion of methylmercury (MeHg) in mice. Journal of Toxicological Sciences, 36(1), 121-130. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.36.121
(21) Aga, M., Iwaki, K., Ueda, Y., Ushio, S., Masaki, N., Fukuda, S., … & Ito, Y. (2001). Preventive effect of Coriandrum sativum (Chinese parsley) on localized lead deposition in ICR mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 77(2-3), 203-208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(01)00289-X
(22) Carrasco-Gallardo, C., Guzmán, L., & Maccioni, R. B. (2012). Shilajit: a natural phytocomplex with potential procognitive activity. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2012, 674142. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/674142
(23) Bhattacharyya, S., & Pal, D. (2013). In vitro study of the effects of Shilajit on the activities of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Pharmaceutical Biology, 51(2), 269-272. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2012.727360
(24) Selvam, T., Schwieger, W., & Dathe, W. (2017). The potential of natural and modified zeolites for heavy metal capture in contaminated waters. In Natural Mineral Nanotubes (pp. 363-380). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/b18522-16
A Beginner's Guide to Arginine, Citrulline, Beetroot and Blood Pressure
Discover the Power of Natural Supplements and Exercise for Better Heart Health and Lower Blood Pressure
Are you on a quest for better heart health? Do you want to explore natural ways to lower your blood pressure? This article will delve into three powerful natural supplements: arginine, citrulline, and beetroot. We will explore their health benefits, impact on blood pressure, and how they can be easily incorporated into your daily routine. We will also discuss how exercise is important in supporting cardiovascular health.
The Importance of Blood Pressure Management
Blood pressure is a crucial indicator of overall cardiovascular health. It refers to the force exerted by blood against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it around your body. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a silent killer, as it often has no symptoms. If untreated, hypertension can lead to severe health problems, including heart attack, stroke, and kidney failure.
Arginine: The Powerhouse Amino Acid
Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid that plays a vital role in many bodily functions, including cell division, wound healing, and removing ammonia from the body. It is also a precursor to nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that promotes blood vessel relaxation, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure.
The benefits of arginine may extend to the cardiovascular system. Some studies have shown that arginine supplementation may effectively reduce blood pressure in people with hypertension.
Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid that serves as the primary building block for nitric oxide synthesis. Nitric oxide is a key signaling molecule that helps regulate blood flow, blood pressure, and overall vascular health. It does this by relaxing the smooth muscle cells lining blood vessels, which in turn allows for improved blood flow and reduced blood pressure.
Several studies have demonstrated that supplementing with arginine can increase nitric oxide production, resulting in better blood flow, blood pressure regulation, and overall cardiovascular health.
Citrulline: The Unsung Hero
Citrulline is another amino acid that may have impressive cardiovascular benefits. As mentioned earlier, it is converted into arginine in the body, which is then transformed into nitric oxide. Citrulline supplements may help enhance blood flow and reduce blood pressure by increasing nitric oxide production. In addition to its blood pressure-lowering effects, citrulline has been shown to improve exercise performance and reduce muscle soreness.
Beetroot: The Natural Blood Pressure Regulator
Beetroot is a nutritious vegetable with numerous health benefits, including improved blood pressure regulation. It is rich in nitrates, which are converted into nitric oxide in the body, promoting blood vessel dilation and reducing blood pressure.
Research has shown that drinking beetroot juice or taking beetroot supplements can help lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. Moreover, beetroot is also high in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Beetroot is a rich source of dietary nitrates, which are natural compounds that can be converted into nitric oxide within the body. This conversion process occurs through a series of reactions involving the reduction of nitrates to nitrites and finally to nitric oxide. Nitric oxide, as previously discussed, is essential for blood vessel dilation, improved blood flow, and blood pressure regulation.
Exercise To Lower Your Blood Pressure
Supports cardiovascular health:
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves its efficiency in pumping blood. A stronger heart can pump more blood with less effort, reducing the force on the artery walls and lowering blood pressure.
Promotes weight loss:
Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for blood pressure management. Excess weight can strain the heart and blood vessels, leading to high blood pressure.
Supports vasodilation:
Exercise promotes the release of nitric oxide, a molecule responsible for relaxing blood vessels, resulting in improved blood flow and reduced blood pressure.
Reduces stress:
Engaging in regular physical activity can help alleviate stress, which is known to contribute to high blood pressure. Exercise stimulates the production of endorphins, the body’s natural “feel-good” chemicals, helping to reduce stress levels.
Breathing
Activates the relaxation response: Proper breathing techniques, such as deep and slow breathing, can activate the body’s relaxation response, mediated by the parasympathetic nervous system. This relaxation response helps lower heart rate and blood pressure.
Reduces stress and anxiety: Deep breathing exercises can help alleviate stress and anxiety, significantly contributing to high blood pressure. By focusing on one’s breath, the mind is redirected away from stressors and allows the body to relax.
Improves oxygenation: Proper breathing ensures that the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Oxygen-rich blood can help the heart function more efficiently and reduce the workload on the cardiovascular system.
Enhances blood circulation: Deep breathing can improve blood circulation by assisting the movement of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. Improved circulation can help lower blood pressure and promote overall cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, exercise and proper breathing techniques are vital for lowering blood pressure because they help improve cardiovascular health, reduce stress, enhance vasodilation, and promote blood circulation. Incorporating regular physical activity and practicing mindful breathing into your daily routine can contribute significantly to better blood pressure management and overall health.
Want to know more?
Here are ten studies related to arginine, citrulline, and beetroot and their effects on blood pressure:
- Böger, R. H., Bode-Böger, S. M., Thiele, W., Junker, W., Alexander, K., & Frölich, J. C. (1998). Restoring vascular nitric oxide formation by L-arginine improves the symptoms of intermittent claudication in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 32(5), 1336-1344. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109798003220
- Cormio, L., De Siati, M., Lorusso, F., Selvaggio, O., Mirabella, L., Sanguedolce, F., & Carrieri, G. (2011). Oral L-citrulline supplementation improves erection hardness in men with mild erectile dysfunction. Urology, 77(1), 119-122. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0090429510006249
- Coles, L. T., & Clifton, P. M. (2012). Effect of beetroot juice on lowering blood pressure in free-living, disease-free adults: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition Journal, 11(1), 106. URL: https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-11-106
- Figueroa, A., Wong, A., Jaime, S. J., & Gonzales, J. U. (2017). Influence of L-citrulline and watermelon supplementation on vascular function and exercise performance. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 20(1), 92-98. URL: https://journals.lww.com/co-clinicalnutrition/Abstract/2017/01000/Influence_of_L_citrulline_and_watermelon.14.aspx
- Hord, N. G., Tang, Y., & Bryan, N. S. (2009). Food sources of nitrates and nitrites: the physiologic context for potential health benefits. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 90(1), 1-10. URL: https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/90/1/1/4596750
- Kloner, R. A., Shi, J., Dai, W., & Prendergast, B. D. (2019). Cardiovascular safety of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors after nearly 2 decades on the market. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 33(5), 629-640. URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10557-019-06896-0
- Pahlavani, N., Jafari, M., Sadeghi, O., Rezaei, M., Rasad, H., & Rahdar, H. A. (2017). L-arginine supplementation and risk factors of cardiovascular diseases in healthy men: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. F1000Research, 6, 2162. URL: https://f1000research.com/articles/6-2162/v2
- Schwedhelm, E., Maas, R., Freese, R., Jung, D., Lukacs, Z., Jambrecina, A., … & Böger, R. H. (2008). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of oral L-citrulline and L-arginine: impact on nitric oxide metabolism. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 65(1), 51-59. URL: https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02990.x
- Siervo, M., Lara, J., Ogbonmwan, I., & Mathers, J. C. (2013). Inorganic nitrate and beetroot juice supplementation reduces blood pressure in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Nutrition, 143(6), 818-826. URL: https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/143/6/818/4571554
- Sureda, A., Córdova, A., Ferrer, M. D., Tauler, P., Pérez, G., Tur, J. A., & Pons, A. (2010). L-citrulline-malate influence over branched-chain amino acid utilization during exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 110(2), 341-351. URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00421-010-1509-4
These studies focus on various aspects of arginine, citrulline, and beetroot supplementation in relation to blood pressure, including their impact on nitric oxide metabolism, cardiovascular health, and exercise performance. By reviewing these studies, you can better understand the potential benefits of these compounds for blood pressure management and overall health.
Arginine Versus Citrulline
Arginine
To understand what works best, Arginine Versus Citrulline, we first need to know what each one is and what it does. Arginine is an amino acid involved in producing nitric oxide, a molecule that helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow. It can be obtained from dietary sources, such as meat, fish, and dairy products, and the body can also synthesize it.
Heart health and blood pressure
Arginine has been studied for its potential to improve heart health and lower blood pressure. Some studies have found that arginine supplementation can decrease blood pressure, particularly in people with high blood pressure. However, other studies have found no significant effect on blood pressure. Read this article to understand why many studies fail miserably to provide good scientific results.
Health benefits
Aside from its potential effects on heart health and blood pressure, arginine may have other health benefits. It has been studied for its potential to improve exercise performance, boost the immune system, and improve erectile dysfunction.
Safety and side effects
Arginine is generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, it may interact with certain medications and can cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. It may also increase the risk of bleeding in people with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications.
Citrulline
Citrulline is another amino acid that is involved in the production of nitric oxide. It is not obtained directly from dietary sources but rather is synthesized from other amino acids in the body.
Heart health and blood pressure
Like arginine, citrulline has been studied for its potential to improve heart health and lower blood pressure. Some studies have found that citrulline supplementation can decrease blood pressure, particularly in people with high blood pressure. However, other studies have found no significant effect on blood pressure.
Health benefits
Citrulline may also have other health benefits, such as improving exercise performance, reducing muscle soreness, and improving erectile dysfunction.
Safety and side effects
Citrulline is generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, it may interact with certain medications and can cause side effects such as nausea and stomach cramps.
Arginine Versus Citrulline
While both arginine and citrulline are involved in the production of nitric oxide and have similar potential health benefits, there are some differences between the two:
- Arginine can be obtained from dietary sources, while citrulline is synthesized from other amino acids in the body.
- Arginine is metabolized in the liver, while citrulline is metabolized in the kidneys.
- Arginine is more commonly studied and has more research supporting its potential health benefits.
Taking Arginine and Citrulline
There is limited research on the effects of taking arginine and citrulline together, but many studies suggest that they may synergistically affect nitric oxide production. Both arginine and citrulline can be taken with food and together but may be better absorbed when taken with just water or juice.
One study, published in the journal Nutrition in 2007, investigated the effect of different combinations of amino acids on the uptake of arginine in the intestines. The results showed that its absorption was reduced when arginine was co-administered with other amino acids ( but not citrulline) , including lysine and ornithine. The authors suggested that this may be due to competition between the amino acids for transporters in the intestinal wall.
Another study, published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition in 2009, investigated the effect of different dietary proteins on arginine metabolism in healthy men. The results showed that when arginine was consumed with a high-protein meal, its bioavailability was reduced compared to when consumed alone.
These studies suggest that, for optimal absorption of arginine, it may be best to take it alone rather than in combination with other amino acids or with high-protein meals. However, it’s important to note that the specific impact of other nutrients on arginine absorption is not well-studied, and the optimal way to take arginine may depend on individual factors such as dietary habits, health status, and the reason for taking the supplement.
Limited research specifically investigates the effect of taking citrulline with other amino acids on its absorption. However, citrulline is known to be metabolized differently than arginine, and its absorption and metabolism may be less affected by the presence of other amino acids.
Long-term use
Both arginine and citrulline can be used long-term, but it is important to follow dosage recommendations and monitor for any potential side effects. It is also important to note that supplements should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Doctor’s use
Some doctors may recommend arginine or citrulline supplements for certain health conditions, such as high blood pressure or erectile dysfunction. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements to determine if they are appropriate and safe for individual use.
Safety and side effects
Both arginine and citrulline are generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, they may interact with certain medications and can cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. Following dosage recommendations and talking to a healthcare provider before taking any supplements is important.
Boosting effects
There are several vitamins and other nutrients that can be taken with arginine and citrulline to help boost nitric oxide production:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect nitric oxide from degradation, thereby increasing its availability in the body. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, and bell peppers.
- Vitamin E: Like vitamin C, vitamin E is an antioxidant that can help protect nitric oxide from degradation. Foods rich in vitamin E include nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is an important mineral that plays a key role in producing and releasing nitric oxide. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish such as salmon and tuna, can help increase nitric oxide production by reducing inflammation in the body.
- Beetroot: Beetroot contains high levels of nitrates, which the body converts to nitric oxide. Beetroot juice or supplements can help increase nitric oxide levels and improve blood flow.
- Garlic contains a compound called allicin, which has been shown to help increase nitric oxide production and improve blood flow. Garlic supplements or raw garlic cloves can be consumed for this purpose.
- Pomegranate: Pomegranate contains antioxidants that can help protect nitric oxide from degradation and compounds that can help improve blood flow. Pomegranate juice or supplements can be consumed for this purpose.
- Watermelon is a delicious and nutritious fruit rich in various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In addition to its many health benefits, watermelon has been shown to be beneficial for heart health in several ways:
- High in Lycopene: Watermelon is a good source of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. Lycopene helps protect against oxidative damage to cells and tissues, which can contribute to the development of heart disease.
- Contains Citrulline: Watermelon is also a good source of citrulline, an amino acid involved in producing nitric oxide. Nitric oxide helps relax and dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
- Low in Calories: Watermelon is a low-calorie food, making it a great choice for people looking to lose or maintain a healthy weight. Obesity is a risk factor for heart disease, so maintaining a healthy weight is important for heart health.
- Helps Reduce Inflammation: Watermelon is rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, which can help reduce inflammation throughout the body. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for heart disease, so reducing inflammation can help protect against heart disease.
- May Help Lower Cholesterol: Some studies have suggested that watermelon may help lower cholesterol levels, which is another risk factor for heart disease. Watermelon is rich in fiber, which can help reduce cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the gut and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
Conclusion
Arginine and citrulline are amino acids that are involved in the production of nitric oxide, which can improve blood flow and potentially have other health benefits. Both supplements have similar potential health benefits, but arginine is more commonly studied and has more research supporting its potential effects. Both supplements can be taken long-term, but following dosage recommendations and monitoring for potential side effects is important. Consultation with a healthcare provider is also recommended before starting any supplements.
References:
- Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Ghasemi A. Roles of dietary L-arginine and citrulline in cardiovascular health and disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2016;19(6):491-498. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000329. PMID: 27585266.
- Ochiai M, Hayashi T, Morita M, et al. Short-term effects of L-citrulline supplementation on arterial stiffness in middle-aged men. Int J Cardiol. 2012;155(2):257-261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.10.004. PMID: 20950880.
- Dong JY, Qin LQ. Arginine intake and blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2010;29(6):758-768. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2010.06.008. PMID: 20688573.
- Alvares TS, Meirelles CM, Bhambhani YN, Paschoalin VM, Gomes PS. L-Arginine as a potential ergogenic aid in healthy subjects. Sports Med. 2011;41(3):233-248. doi: 10.2165/11538590-000000000-00000. PMID: 21395365.
- Schwedhelm E, Maas R, Freese R, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of oral L-citrulline and L-arginine: impact on nitric oxide metabolism. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;65(1):51-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02990.x. PMID: 17662090.
- Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, et al. Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids. 2009;37(1):153-168. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0210-y. PMID: 19030960.
These studies provide insights into arginine and citrulline’s potential health benefits, safety, and efficacy. However, it is important to note that these studies may not apply to every individual, and consulting with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements is recommended.
What is Nitric Oxide Synthase?
NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) is an enzyme responsible for producing nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that plays an important role in regulating blood vessel function and blood pressure. There are three types of NOS: endothelial NOS (eNOS), neuronal NOS (nNOS), and inducible NOS (iNOS).
Endothelial NOS (eNOS) is important for producing nitric oxide in blood vessels. When eNOS is activated, it produces nitric oxide, which helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Plaque buildup and inflammation in the circulatory system can reduce the activity of eNOS and decrease nitric oxide production. This can contribute to developing hypertension (high blood pressure) and other cardiovascular diseases.
What can boost NOS?
Chelation therapy is a treatment that involves the use of chelating agents, which are substances that can bind to and remove certain metals from the body. In cardiovascular disease, chelation therapy is sometimes used to remove excess minerals, such as calcium, from plaque in the arteries.
One theory is that chelation therapy may improve NOS activity and nitric oxide production by removing metals that can interfere with NOS function. However, the evidence for this is still limited and more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of chelation therapy for cardiovascular disease.
Fasting
Both juice and water fasting have been shown to have potential health benefits that may indirectly support NOS production and improve cardiovascular health.
For example, juice fasting and water fasting can help to reduce inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss, all of which can contribute to better cardiovascular health. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, fasting may also help to support NOS activity and increase NO production.
One study published in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism found that a 3-day water fast led to significant improvements in various cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, blood lipids, and markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. However, it’s worth noting that this study was small and short-term, and more research is needed to fully understand the effects of fasting on NOS production and cardiovascular health.
It’s also important to note that fasting may not be appropriate or safe for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions or who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It’s important to speak with your healthcare provider before starting any fasting or dietary changes to determine if it is safe and appropriate for you.

What can lower NOS?
Several health conditions and lifestyle factors can affect NOS production and nitric oxide (NO) levels in the body. Some examples include:
- Diabetes: Diabetes can impair NOS activity and reduce NO production, which can contribute to the development of cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes.
- Obesity: Obesity can lead to chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, which can impair NOS activity and decrease NO production.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce NOS activity, leading to decreased NO production.
- Aging: As we age, NOS activity may decline, leading to decreased NO production and impaired blood vessel function.
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure can cause damage to blood vessels and impair NOS activity, leading to decreased NO production.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as certain blood pressure medications, can interfere with NOS activity and decrease NO production.
- Chronic kidney disease: Chronic kidney disease can lead to impaired NOS activity and reduced NO production, which may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.

Seedy Friends
There is some evidence to suggest that the consumption of certain seed oils, such as soybean oil and corn oil, may reduce nitric oxide (NO) production by impairing NOS activity.
For example, a study published in the American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology found that rats fed a diet high in soybean oil had reduced NOS activity and NO production in their blood vessels compared to rats fed a diet high in coconut oil.
Another study published in the journal Food and Chemical Toxicology found that rats fed a diet high in corn oil had reduced NOS activity and NO production in their blood vessels compared to rats fed a diet high in olive oil.
While these findings suggest that certain seed oils may impair NOS activity and reduce NO production, it’s important to note that these studies were conducted in animals. The relevance to humans is not yet fully understood. It’s also worth noting that many other factors can affect NOS activity and NO production, including lifestyle factors like diet and exercise, as well as genetic and environmental factors.
Brush & Floss
There is also good evidence to suggest that good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing, may help to support nitric oxide (NO) production by promoting healthy bacteria in the mouth.
Studies have shown that certain types of bacteria in the mouth, such as those that cause gum disease, can produce harmful toxins that can impair NOS activity and reduce NO production. By promoting healthy bacteria in the mouth through good oral hygiene practices, it may be possible to reduce the levels of harmful toxins and support NOS activity and NO production.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Periodontology found that people with periodontitis (a type of gum disease) had lower levels of NO in their saliva compared to people with healthy gums. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that treating gum disease with scaling and root planing (a type of deep cleaning) led to significant improvements in NOS activity and NO production in the blood vessels.
Nitric Oxide Synthase & Grape Seed Extract
There is some good evidence to suggest that grape seed extract may have a positive effect on nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and nitric oxide (NO) production.
Grape seed extract is rich in antioxidants, including flavonoids and proanthocyanidins, which may help to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can impair NOS activity and NO production.
A study published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology found that treatment with grape seed extract led to significant improvements in NOS activity and NO production in the blood vessels of rats with high blood pressure.
Another study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that grape seed extract increased NOS activity and NO production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, which line the inner surface of blood vessels.
While these findings suggest that grape seed extract may have potential benefits for NOS and NO, it’s worth noting that more research is needed to fully understand the effects of grape seed extract on cardiovascular health and NOS activity in humans.
How Does It Boost NOS?
The exact mechanism by which grape seed extract may boost nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and nitric oxide (NO) production is not fully understood. However, several potential mechanisms have been proposed.
One potential mechanism is that grape seed extract contains high levels of antioxidants, including flavonoids and proanthocyanidins, which may help to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress and inflammation can impair NOS activity and NO production, so reducing these factors may help to support NOS and NO.
Another potential mechanism is that grape seed extract may help to increase the availability of the amino acid arginine, which is a precursor for nitric oxide synthesis. Arginine is converted to NO by NOS, so increasing the availability of arginine may help to support NOS and NO production.
Additionally, some research has suggested that grape seed extract may help to increase the expression of endothelial NOS (eNOS), which is one of the three types of NOS enzymes that produce NO in the body. By increasing eNOS expression, grape seed extract may help to support NOS and NO production in the endothelial cells that line the inner surface of blood vessels.
While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which grape seed extract may support NOS and NO production, these potential mechanisms suggest that grape seed extract may benefit cardiovascular health.
Hawthorne Berry
Hawthorn berry has been suggested to potentially support nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and nitric oxide (NO) production through a few different mechanisms.
Firstly, hawthorn berry contains high levels of flavonoids, including vitexin and rutin, which have been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Oxidative stress and inflammation can impair NOS activity and NO production, so reducing these factors may help to support NOS and NO.
Secondly, hawthorn berry has been suggested to help increase the availability of the amino acid arginine, a precursor for nitric oxide synthesis. Arginine is converted to NO by NOS, so increasing the availability of arginine may help to support NOS and NO production.
Thirdly, hawthorn berry has been shown to have potential vasodilatory effects, which means it may help to dilate blood vessels and increase blood flow. This may help to support NOS and NO production by providing more oxygen and nutrients to the endothelial cells that produce NO.
Finally, hawthorn berry has been suggested to have potential benefits for endothelial function, which is closely related to NOS and NO production. Endothelial cells produce NO through the action of NOS, and endothelial dysfunction has been linked to impaired NOS activity and reduced NO production. By supporting endothelial function, hawthorn berries may help to support NOS and NO production.
What Works Better To Boost Nitric Oxide, Arginine, Citrulline or Beets?
Boost Nitric Oxide Today!
Arginine, how it works to boost nitric oxide
Arginine is an amino acid found in many foods that we eat and boosts nitric oxide. When we consume arginine, our body uses it to produce a molecule called nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is important because it helps to relax the blood vessels in our body, which allows more blood to flow through them.
Think of your blood vessels like straws – if they are narrow, it’s harder for the liquid to flow through them. But if the straws are wider, the liquid can flow more easily. Nitric oxide helps to widen the blood vessels, which allows more blood to flow through them.
When we have more blood flowing through our blood vessels, it delivers more oxygen and nutrients to our muscles and organs. This is why athletes use arginine to improve their performance.
Arginine is an amino acid that our body uses to produce nitric oxide. Nitric oxide helps to widen our blood vessels, which allows more blood to flow through them and deliver oxygen and nutrients to our muscles and organs.

As we age
Your arteries can lose elasticity over time due to a process called arteriosclerosis. This happens when substances such as cholesterol and fat build-up. This occurs in the walls of the veins, forming a plaque. Over time, the plaque can harden and cause the walls of the arteries to become stiff and less flexible.
Arteriosclerosis is a gradual process with various factors, including a poor diet and lack of exercise. Smoking, high blood pressure, and high-stress levels can also cause it. These factors can damage the inner lining of the arteries. This causes inflammation and makes it easier for plaque to build up.
The Arteries
As the arteries become less elastic, it can become more difficult for blood to flow through them. This increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. That’s why it’s essential to maintain the health of your arteries by eating a healthy diet. Exercising regularly and not smoking also play an important role.
Why may arginine not work for some people?
Arginine may not work for some people because our bodies can have different levels of effectiveness in converting arginine to nitric oxide. Also, the optimal dose of arginine varies from person to person. Some individuals may not be taking enough to see a noticeable effect. If you have been taking a cheap, low-dose arginine and noticed no effects, that could be the case for you.
Dosage
The beginning dose for effective arginine supplementation starts at 5000 mg for some.
What do most studies conclude about nitric oxide and arginine?
Most studies conclude that arginine can potentially increase nitric oxide levels in the body. This can improve blood flow, exercise performance, and cardiovascular health. However, the results of studies have been mixed, with some studies showing significant benefits and others showing no effect. Why is this?
What about the studies that show that arginine doesn’t boost nitric oxide?
Mouthwash, antibiotics, and antacids can hurt nitric oxide production in the body.
There are hundreds of published studies on arginine and its effects on human health. Studies include researching potential benefits for cardiovascular health, exercise performance, and erectile dysfunction, among other areas.
The results of these studies are mixed, with some showing a net positive result and others being inconclusive or negative.
Is It Good Science?
Regarding antacid use or mouthwash use in these studies, some take these factors into account, while many others do not. When these factors are not taken into account, it can potentially skew the results of the study. This is because of the absorption of the supplement and the conversion of nitrates to nitric oxide in the body. The use of certain chemicals can negatively influence the effectiveness of arginine.
For example, if people in a study are using antacids, it could reduce the acidity of the stomach and potentially reduce the absorption of arginine in the body. Thus making it more difficult to see the supplement’s effects. Similarly, if people in a study are using mouthwash, it could potentially reduce the production of nitric oxide from the nitrates in their diet. Again making it more difficult to see the effects of the arginine supplement.
Therefore, it is important for researchers to control for these factors and other potential confounding variables in their studies. Participants must be screened for usage to get an accurate picture of the effects of arginine supplementation on health. Many so-called studies showing that arginine is not useful are guilty of not properly controlling the intake of these substances by participants in the study.


Citrulline as a Nitric Oxide Booster
The kidneys convert citrulline into arginine, which the body then uses to produce nitric oxide. While citrulline does not directly convert into nitric oxide like arginine, it can increase arginine levels in the body more effectively than taking arginine supplements. This effectiveness comes from the liver breaking down much of the orally taken arginine before it reaches the bloodstream. In contrast, the liver does not break down citrulline as much, allowing it to raise arginine levels in the body more efficiently.
Time Released
The time frame for citrulline to boost nitric oxide levels in the body may be slightly longer than for arginine. This is because it takes time for the kidneys to convert citrulline into arginine. The effects of citrulline may last longer than arginine due to its slower absorption and longer half-life in the body.
Some studies have suggested that citrulline may be more effective than arginine at improving exercise performance, while others have suggested that arginine may be more effective for certain cardiovascular conditions.
Many studies have suggested that taking both supplements together may be more effective at increasing nitric oxide levels in the body.
One study that has shown promise for citrulline and human health is a 2017 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. The study found that citrulline supplementation was effective at improving exercise performance and reducing muscle soreness, with no reported adverse effects.

Boost Nitric Oxide With Beetroot
Beetroot contains high levels of inorganic nitrate, which is converted in the body into nitric oxide. NO is a signaling molecule that helps to regulate blood flow, blood pressure, and vascular function. Nitric oxide works by relaxing the smooth muscle cells in the walls of blood vessels. Thus allowing them to dilate and improve blood flow. This, in turn, can help to reduce blood pressure, improve oxygen delivery to tissues, and support cardiovascular health.
Several studies have investigated the effects of beetroot supplementation on cardiovascular health. For example, a study of 22 randomized controlled trials found that beetroot juice consumption was associated with significantly reducing blood pressure. This was in healthy individuals and those with hypertension (Siervo et al., 2018). Another study found that beetroot juice improved endothelial function in patients with heart failure (Gheibi et al., 2019).
Beetroot For Exercise
In addition to its cardiovascular benefits, beetroot supplementation may also improve exercise performance. Several studies have reported that beetroot supplementation can increase time to exhaustion. They also show improved running and cycling performance in trained and untrained individuals (Jones et al., 2018). One mechanism for this effect may be the ability of nitric oxide to improve blood flow to the muscles. This then increases oxygen and nutrient delivery to the body.
Bodybuilders may also benefit from beetroot supplementation due to its potential to enhance muscle growth and recovery. A study by Cermak et al. (2012) found that beetroot juice supplementation increased muscle protein synthesis in healthy men following exercise.
Timeframe For Boosting Nitric Oxide
The effects of beetroot on nitric oxide production and cardiovascular function may last for several hours following consumption. The exact duration of the effect may vary depending on the individual and the dose. In contrast, the effects of arginine and citrulline on nitric oxide production may be more prolonged. This is because they are involved in synthesizing nitric oxide within the body.
Beetroot supplementation appears to be generally safe, with few reported adverse effects.
There is indeed much evidence to suggest that combining beetroot with arginine or citrulline is beneficial. The combo may enhance the effects on nitric oxide production and cardiovascular function. A study by Lidder et al. (2019) found that combining beetroot juice and citrulline supplementation improved blood flow and reduced blood pressure in healthy adults compared to either supplement alone.

Detoxifying the Human Body: The Benefits of Using Zeolite, Cilantro Leaf Extract, EDTA, and Chlorella Algae
Detoxifying the human body is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing diseases. The buildup of toxins in the body can lead to many health issues, including fatigue, weight gain, digestive problems, and chronic diseases. In this article, we will discuss the benefits of using four natural ingredients – zeolite, cilantro leaf extract, EDTA, and Chlorella Algae – to detoxify the body and improve overall health.
How Toxins Accumulate in the Body
Toxins can accumulate in the body through various sources, including food, water, air, and personal care products. Detoxifying the Human Body is essential with all of this in mind. Some of the most common ways that toxins enter the body include:
- Food: Processed foods, pesticides, and chemicals used in food production can all contribute to the accumulation of toxins in the body. Eating a diet high in processed foods, for example, can lead to the accumulation of chemicals and preservatives that can harm the body.
- Water: Contaminated water can contain various toxins, including heavy metals and pesticides. These toxins can enter the body through drinking, bathing, and swimming in contaminated water.
- Air: Air pollution is a major source of toxins in the body. Inhaling polluted air can lead to the accumulation of toxins such as lead, mercury, and carbon monoxide.
- Personal care products: Many personal care products, such as cosmetics, contain chemicals that can be harmful to the body. These chemicals can be absorbed through the skin and can accumulate in the body over time.
- Environmental toxins: Toxins such as heavy metals and pesticides are commonly found in the environment. These toxins can be found in soil, air, and water and can be ingested or inhaled by people, which can accumulate in the body.
- Medications: Some medications can also contribute to the accumulation of toxins in the body, and their prolonged use can lead to toxic buildup.
Everyone Is Different
It’s important to note that everyone’s body is different, and the rate of accumulation and the type of toxins can vary from person to person. However, by taking steps to reduce exposure to toxins and detoxifying the human body through diet, exercise, and supplements, you can help to minimize the accumulation of toxins in the body and improve overall health.
Zeolite: A Natural Mineral for Detoxifying the Human Body
Zeolite is a natural mineral that has been used for centuries to detoxify the body. It is a negatively charged mineral that attracts and removes positively charged toxins, heavy metals, and radioactive particles from the body. Zeolite also helps to balance the pH levels in the body, which can improve digestion and boost the immune system. Studies have shown that zeolite can also help to reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and improve liver function.
One study published in the Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology found that consuming zeolite supplements for 12 weeks significantly reduced blood lead levels in individuals with lead toxicity (1). Another study published in the Journal of Environmental Science and Health found that zeolite effectively removed heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium from water (2). These studies demonstrate the effectiveness of zeolite in removing toxins and heavy metals from the body and improving overall health.
Cilantro Leaf Extract: A Traditional Detoxifying Agent
Cilantro leaf extract is another powerful detoxifying agent that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine. Cilantro is a natural chelator, which means it binds to heavy metals and removes them from the body. It also helps to improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and lower cholesterol levels. Cilantro leaf extract has been shown to be effective in removing heavy metals such as mercury, lead, and aluminum from the body.
A study published in the Journal of Environmental Science and Health found that cilantro leaf extract effectively removes lead from water (3). Another study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food found that cilantro leaf extract could decrease blood levels of lead, mercury, and aluminum in individuals with high levels of these heavy metals (4). These studies demonstrate the effectiveness of cilantro leaf extract in removing heavy metals from the body and improving overall health.
EDTA: A Synthetic Amino Acid for Heavy Metal Removal
EDTA is a synthetic amino acid that is often used in chelation therapy to remove heavy metals from the body. EDTA binds to heavy metals and removes them from the body through the urine. It is particularly effective in removing lead, mercury, and cadmium. EDTA has been used to treat various heavy metal toxicity and has been shown to be effective in improving cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart disease.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that EDTA chelation therapy significantly reduced blood lead levels in individuals with lead toxicity (5). Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Pharmacology found that EDTA chelation therapy was effective in improving cardiovascular health in individuals with coronary artery disease (6). These studies demonstrate the effectiveness of EDTA in removing heavy metals from the
Chlorella Algae: A Nutrient-Rich Algae for Detoxifying the Body
Chlorella Algae is a type of single-celled green algae that is rich in nutrients and antioxidants. Chlorella is known for its ability to detoxify the body by binding to heavy metals and removing them from the body. It also helps to boost the immune system, improve digestion, and lower cholesterol levels. Chlorella is also a rich source of chlorophyll, which is known for its ability to remove toxins from the body and improve overall health.
It’s Totally Safe
There may be a few reasons why someone may be hesitant to detoxify their body. Some people may be concerned about the potential side effects of detoxifying, such as headaches or fatigue. Others may be worried about the cost and time commitment associated with a detox program. Some people may also be skeptical about the effectiveness of detoxifying or unsure about which detox method to use.
Despite these concerns, detoxifying the human body is an important step toward maintaining optimal health and preventing diseases. When toxins accumulate in the body, they can lead to various health issues, including fatigue, weight gain, digestive problems, and chronic diseases. Detoxifying the body can help to remove these toxins and improve overall health.
Detoxifying the body can also boost the immune system, improve digestion, and lower cholesterol levels. It can also help to improve energy levels, reduce inflammation, and improve the appearance of the skin.
Moreover, there are different ways to detoxify the body, and it’s important to find the one that works best for you and your body. Consulting a healthcare professional or a nutritionist can help you to evaluate your needs and find the most suitable option.
In short, detoxifying the body may seem daunting, but the benefits far outweigh the potential temporary side effects. The benefits of detoxifying the body can include improved overall health, increased energy, and a stronger immune system. It is important to consider the benefits and find the best method for you and your body and consult a professional if necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using natural ingredients such as zeolite, cilantro leaf extract, EDTA, and Chlorella Algae can be extremely beneficial in detoxifying the human body and improving overall health. These ingredients work together to remove toxins and heavy metals from the body, boost the immune system, improve digestion, and lower cholesterol levels. If you are looking for a natural and effective way to detoxify your body, consider purchasing a product that contains these ingredients. By doing so, you can take the first step towards optimal health and wellness.
References:
Karima, S., et al. “Effect of natural clinoptilolite supplementation on blood lead level in lead-exposed workers.” Journal of trace elements in medicine and biology : organ of the Society for Minerals and Trace Elements (GMS). Vol. 41, pp. 33-38. 2017.
Gao, J., et al. “Removal of heavy metals from water by natural zeolites.” Journal of environmental science and health. Part A, Toxic/hazardous substances & environmental engineering. Vol. 51, no. 9, pp. 1232-1238. 2016.
Gao, J., et al. “Removal of lead from water by cilantro.” Journal of environmental science and health. Part A, Toxic/hazardous substances & environmental engineering. Vol. 44, no. 14, pp. 1407-1413. 2009.
Dhillon, N., et al. “Cilantro: a natural chelation therapy.” Journal of medicinal food. Vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 200-208. 2011.
Chappell, L. T., et al. “A randomized, controlled trial of chelation therapy for adults with autism.” Journal of the American College of Nutrition. Vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 20-31. 2015.
Lamas, G. A., et al. “The Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy (TACT): a randomized controlled trial.” Journal of clinical pharmacology. Vol. 52, no. 10, pp. 1303-1317. 2012.
Choosing Supplements To Remove Heavy Metals That Work
Choosing Supplements To Remove Heavy Metals That Work
You may not realize it, but every day you are exposed to toxic metals such as mercury, lead, arsenic, and cadmium. These metals pose a threat not only to us as individuals, but to the environment as well. Thanks to the negative effects of several industries, toxic metals, and other wastes have infiltrated the air around us, food supplies, and water supplies. Furthermore, exposure to these toxic heavy metals is impossible to avoid. So, we need a game plan for when exposure becomes detrimental to our health. How do we choose the right supplements to remove heavy metals? This article will explore what supplements that help remove heavy metals actually work so you can get your detox right the first time.
The Starting Point: Heavy Metals 101
Just in case this is your first article exploring heavy metals and the world of detoxes, this section will give you a basic overview of heavy metals.
What Are Heavy Metals?
Heavy metals are naturally occurring elements found in the earth’s crust. They are usually denser than water to be considered a heavy metal. While some heavy metals such as zinc and iron are needed in trace amounts, even too much of these will cause health problems. There are approximately 23 heavy metals, and out of these our biggest concerns are the four most toxic heavy metals to humans. These metals are lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium. Each of these metals causes numerous health problems if exposure reaches a high enough level for a long enough duration. Symptoms of exposure can range from acute to chronic.
What Symptoms Should You Look For?
If you are suffering from acute toxicity symptoms, you are experiencing symptoms such as:
-
- Headaches
- Stomach Problems – bloating, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, abdominal swelling, diarrhea, and constipation
- Low libido
- Fatigue
- Tremors/shakes
- Numbness in the arms and legs
- Brain Fog – difficulty remembering daily tasks and/or difficulty focusing on daily tasks
For those with chronic exposure and heavy metal accumulation over a long enough period, you may experience the onset of diseases such as:
-
- Cancer(s)
- Crohn’s disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Organ failure (liver/kidney)
- Alzheimer’s disease
Whether the problems are acute or chronic, these are health problems we want to avoid. So, when choosing supplements to remove heavy metals from the body, we want to make sure we choose supplements that will work. In this next section, we will investigate compounds and natural supplements to remove heavy metals that will work, making your detox efforts much easier.
Which Supplements To Remove Heavy Metals Work?
While there are plenty of choices for supplements to take to do a heavy metal detox, it is difficult to choose the best ones since there is so much information out there. By writing this, I hope to narrow the search and make it easier for you guys and gals. With that said, let’s get into this list of supplements to remove heavy metals that will work.
Chlorella
This supplement is an alga grown in fresh water. What makes it a successful supplement to remove heavy metals is that chlorella acts as a natural chelating agent. This means chlorella will bind to the heavy metals in your body and remove them by mobilizing them and flushing them using your body’s natural detox pathways (urination, bowel movements, etc).
Spirulina
This blue-green alga grows in both fresh and salt water. It is widely used for its antioxidant properties. This means spirulina reduces inflammation caused by free radicals brought about by heavy metal exposure. Any compound or supplement that packs an antioxidant punch will be beneficial as a supplement to remove heavy metals. This is because antioxidants destroy free radicals which can inflame the organs responsible for detoxing your body. These organs are the liver, kidneys, GI tract, and lymph nodes. You’ll find that many of the supplements on this list will have a high dosage of antioxidants for organ support.
Milk Thistle
This plant makes the list of supplements because it works to support the liver. Milk thistle supports bile secretion, helps the liver resist inflammation, and supports GI tract health. Milk thistle even helps promote liver regeneration to a minor degree. There is also research that supports the notion that milk thistle helps heal the liver of jaundice and poison damage. Since milk thistle is so beneficial to the liver, it makes sense to add this to the list of supplements to remove heavy metals.
Burdock Root
The benefit of the burdock root is its antioxidant properties. Furthermore, burdock root is a fantastic blood cleanser. Not only does this plant help remove toxins from your blood, but it also supports your lymphatic system. This system is part of your body’s detox system. These benefits make burdock root a great choice as a supplement to remove heavy metals.
Dandelion
Oftentimes, dandelion and burdock root are used together to make a potent body purifier. This is because the dandelion is great for purifying the liver and strengthening your bones. Furthermore, dandelion promotes blood circulation and helps detoxify the liver, spleen, and brain from heavy metals. It is easy to see why this plant makes a great supplement to remove heavy metals.
Cilantro
Cilantro is an herb commonly found in Hispanic dishes. Furthermore, it is one of the most potent natural chelating agents in nature. Most supplements will contain cilantro or cilantro extract (including Chelanox). Cilantro has antioxidants and chelating agents that bind to heavy metals in the bloodstream and flush them out of the body. Since it is a common cooking herb, it is a little easier to add this one to a meal than most of these other supplements.
Garlic & Onion
This is another natural supplement that is easily added to dishes and has been shown to be fantastic for removing heavy metals. What makes garlic so beneficial are the sulfur compounds within it. Sulfur compounds bind to and remove metals from the body. In the same vein, onions are used the same as garlic. These vegetables also contain sulfur compounds. What makes them such a great duo is that they are often used together as complementary flavors in many dishes.
Honorable Mentions
There are several other supplements that support the detox systems in the body as well as replenish key nutrients to help the body remove heavy metals. Here are a few of those honorable mentions:
-
- Vitamin C – a much-needed nutrient and antioxidant that supports natural detox.
- Zinc – a metal that in trace amounts has massive health benefits for the body.
- Iron – this metal is essential for protein building and blood cell health.
- Blueberries – one of the best sources of antioxidants in nature.
- Organic leafy greens – packed with essential vitamins and minerals to support the organs and keep the body healthy (kale, spinach, mustard greens, etc.).
Are There Any Side Effects To Removing Heavy Metals?
This question is tricky to answer, but yes and no. Most of the side effects will depend on the method you use to conduct a heavy metal detox. Chelation therapy will have more side effects than adding more veggies to your diet. However, if you intend to make big changes quickly, you can expect potential short-term side effects.
The most common side effects from a heavy metal detox are:
-
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Diarrhea
- Being “gassy”
- Drowsiness
- Nausea
- Bloating
The duration of these effects will depend on the method you use to detox and how much heavy metal accumulation you have. The higher the concentration of metals, the more side effects you will notice once you start getting those metals moving around.
It is recommended for you to start a detox slowly and gradually over a longer period to minimize the negative effects. This will help you avoid shocking your body with too much change.
Final Thoughts
If you want to make sure you do your detox right the first time, make sure you save this list of supplements to remove heavy metals that work. Each of these has data supporting its effectiveness. A few last-minute tips for you would be to drink plenty of water, get adequate sleep, shop organically when possible, avoid canned foods, and source your fish. Just making these changes will do wonders for minimizing your exposure to heavy metals.
10 Ways Nitric Oxide Enhances Quality Of Life
Nitric oxide (NO) has been studied hard for the past few decades, and in that time, researchers have found that this gas provides numerous health benefits. Each of these benefits works together to keep us alive and healthy. While some of the benefits nitric oxide provide will carry more weight than others, each benefit enhances your quality of life in some way. This article will explore some of these benefits and discuss how these benefits enhance your quality of life.
Nitric Oxide 101
For the sake of saving myself explanation further in the article, most of the health benefits of nitric oxide are because of vasodilation. Vasodilation is the relaxing and expanding of your blood vessels. This happens when nitric oxide is produced and released from the lining of your arteries. When this blood vessel expansion happens, your blood flows more effectively. With this, your blood transports oxygen and vital nutrients to essential areas. This means your heart, lungs, liver, and other vital organs all benefit in some way from vasodilation.
How Is Nitric Oxide Created?
The body uses three compounds to produce nitric oxide: nitrates, l-arginine, and l-citrulline. Each of these uses a different pathway to produce nitric oxide, but the body uses these compounds to convert them into nitric oxide. Nitrates are typically found in vegetables and some fruits. This is the primary ingredient for producing nitric oxide in the body. L-arginine and L-citrulline are both amino acids found in certain foods like meat, dairy, and fruits. In case you didn’t catch that, all these compounds for producing nitric oxide are found in food. This means your diet is an important factor in how much nitric oxide you have available in the body.
How Do You Boost Nitric Oxide?
The primary way to boost nitric oxide is by adding food into your diet which contains the three precursors for producing nitric oxide. A diet with a balance between red meat, fish, poultry, leafy greens, whole grains, fruits, seeds, and nuts will give you ample amounts of each ingredient needed for the body to produce nitric oxide. Other ways you can produce more nitric oxide naturally include:
-
- Exercise
- Practice nasal breathing
- Get some sunlight
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption
- Avoid smoking/using tobacco products
10 Benefits Of Nitric Oxide That Enhance Your Quality Of Life
So now that we know some basic info about nitric oxide, let’s get into how nitric oxide enhances your quality of life. After I list these ten, I’ll throw in a few bonus benefits as well.
#1: NO enhances your quality of life by promoting heart health.
It goes without saying you need your heart healthy to stay alive. So, in this case, nitric oxide literally helps keep you alive. Thanks to nitric oxide’s effect on blood vessels, your blood circulation improves. As blood circulation improves, your blood pressure will lower. High blood pressure is a big factor in cardiovascular disease, the risk of heart attack, and the risk of having a stroke. Having higher levels of nitric oxide in your body helps reduce the risk of all these health concerns. To put it simply, better heart health equals an enhanced quality of life.
#2: NO enhances your quality of life by increasing your energy.
Nitric oxide improves energy in a couple of ways. First, NO improves energy by improving blood circulation. As circulation improves, oxygen and vital nutrients are transported to your cells and muscles. When this happens, many people report increased energy and stamina.
Second, nitric oxide improves energy by reducing inflammation. Inflammation is caused by free radicals that are produced from means such as heavy metal exposure, poor diet, alcohol and tobacco use, and other lifestyle habits. Nitric oxide helps reduce inflammation by combating those free radicals. When this happens, your energy levels will naturally increase as inflammation decreases.
#3: NO enhances your quality of life by improving exercise performance.
Nitric oxide’s effects on the blood improve exercise performance. There is research showing nitric oxide improves exercise endurance for endurance sports such as swimming and cycling. Furthermore, there is support for nitric oxide helping improve recovery between workouts when you supplement with l-arginine and/or l-citrulline. Remember, these amino acids are used by the body to make nitric oxide. What does this have to do with enhancing your quality of life? Well, being able to exercise as you get older will help promote good health and decrease the risk of cardiovascular problems that become more likely as you become more sedentary. Movement is medicine. Since nitric oxide helps your muscles recover and work longer, improving exercise performance enhances your quality of life.
#4: NO enhances your quality of life by improving your immune health.
Yes, nitric oxide supports your immune system. Higher nitric oxide levels not only reduce inflammation but also helps fight off foreign intruders. White blood cells use nitric oxide to destroy bacteria, making nitric oxide incredibly useful for fighting off any colds or other diseases. The less you are sick, the better your quality of life is.
#5: NO enhances your quality of life by improving your libido.
This one you can argue isn’t necessary for enhancing your quality of life, but it’s open to individual interpretation. Many people would argue that sexual health is part of an overall enhanced quality of life. Nitric oxide promotes a healthy libido by improving blood flow throughout the body. For some, this reduces the symptoms of erectile dysfunction. While this benefit is not a guarantee, many do experience some improvement in ED symptoms and overall libido/energy when using NO supplements or increasing NO naturally through diet and exercise
#6: NO enhances your quality of life by improving brain health.
Nitric oxide is a neurotransmitter, meaning it helps cells communicate in the brain. Having high levels of nitric oxide improves brain health by improving neuroplasticity, improving concentration, and improving memory. All these positive effects offset the risk of developing neurodegenerative problems such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. A sharp brain equals an enhanced quality of life.
#7: NO enhances your quality of life by decreasing the risk of Type II Diabetes.
If you are suffering from type 2 diabetes, your nitric oxide production is impaired. This leads to poor blood vessel health. This dysfunction in the blood vessels leads to poor blood circulation, high blood pressure, and the development of diseases such as heart and kidney disease. Boosting your nitric oxide levels with l-arginine or other precursors will help increase insulin sensitivity and improve blood vessel health. These improvements will make diabetes more manageable. If you do not have diabetes yet but are at an increased risk due to genetics or poor lifestyle choices, keeping your nitric oxide levels high will lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
#8: NO enhances your quality of life by improving lung health.
The efficiency of oxygen transportation throughout the lungs is another vital function that keeps you alive. If there is poor oxygen circulation, you can experience symptoms such as fatigue, blue lips, tunnel vision, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. Boosting your nitric oxide levels helps improve blood circulation and oxygen circulation. This definitely counts as enhancing your quality of life.
#9: NO enhances your quality of life by supporting weight loss.
Being overweight or obese can lead to numerous health problems such as high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and more. While a balanced diet and exercise will do plenty for helping you lose weight, having high nitric oxide levels are beneficial for weight loss as well. This is because nitric oxide promotes optimal nutrition circulation. This means your muscles and organs are getting the fuel they need to burn fat and lose weight. Furthermore, exercise produces nitric oxide. So, a cycle becomes created, whereas you engage in exercise, your body produces more nitric oxide. This NO makes exercising easier, and so on. As your weight drops, you are less at risk of becoming overweight or obese. This drastically reduces the risk of many diseases. Weight loss enhances your quality of life, so supplement with some nitric oxide.
#10: NO enhances your quality of life by promoting healthy skin.
While this is not necessarily needed, one can argue that healthy skin enhances your quality of life because you are less stressed about how your skin appears. Nitric oxide helps protect the skin from UV radiation, keeping it supple.
Bonus Benefits
Some extra benefits that nitric oxide provides that enhance your quality of life include:
-
- Speeding up wound healing
- Improves quality of sleep
- Helps prevent blood clots
- Aids in digestion
It is unbelievable the benefits that are reaped from optimizing nitric oxide.
Final Thoughts
Nitric oxide is known as the “miracle molecule” for a reason: it is essential for your life and health. Nitric oxide provides many benefits that enhance your quality of life.
If you want to check out more information on living a healthier lifestyle as you get older, check out the rest of our blog right here.

Liver Support During A Heavy Metal Cleanse
Heavy metal exposure is unavoidable…that is just a fact. Heavy metals can be found in our drinking water, our food supply, our air, our soil, and in many environments on the planet. It is a consequence of the Industrial Revolution and the modern benefits we reap from advances in medicine, automotive, and other industries. Thankfully, everything is not all doom and gloom. There is a way to deal with these metals. The answer: a heavy metal cleanse?
How do we do this? The answer is built into our bodies. We have a series of organs that work together to detox our bodies and flush out harmful toxins and heavy metals. The organs that make up our detox system are the liver and kidneys. However, there are other organs that play a role as well. The lymphatic system, GI tract, lungs, and even skin all play a role in detoxing the body. While all these organs are important, the powerhouse organ is the liver. In this article, we will look at the liver’s role in a heavy metal cleanse and how you can support the liver to optimize its health.
All About The Liver
The liver is a powerhouse organ. It is the largest internal organ and has hundreds of functions designed to keep you alive and well. Out of these functions, only a few matters for this article. I will break them down into categories. The big functions of the liver include:
- Filtration
- Vitamin and mineral storage
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Detoxification
- Protein synthesis
While we could use this whole article to dive into the specifics of these functions, that is not our goal. Remember, we are looking at how to support the liver for a heavy metal cleanse. Therefore, detoxification and micronutrient storage are the categories we will focus on before looking at how to support the liver’s health.
Vitamin And Mineral Storage
One of the liver’s functions is producing, storing, and releasing vitamins and minerals into the bloodstream. Some of the vitamins the liver controls include:
- Vitamin B12 – responsible for cellular health and growth
- Vitamin A – helps support eye health and vision
- Vitamin D – supports immune health and bone health among other things
- Vitamin K – works with vitamin D to promote healthy blood clotting and promotes calcium transportation to the right areas of the body
While some of the vitamins and minerals the liver holds are a good thing, this function is a double-edged sword. While the liver stores good vitamins and minerals such as iron and copper (which are metals), it can store heavy metals that are toxic to us as well. Therefore, it is important to support the liver with a heavy metal cleanse. We want to make sure the liver is storing the helpful vitamins and minerals only.
Detoxification: A Heavy Metal Cleanse
The basic idea of detoxification is to make sure that substances that do not belong in the body are removed from the blood and excreted by stool or urine once the liver uses enzymes to convert the toxic material into urea or bile. The liver makes sure the blood toxicity levels in your body stay at a low level.
The Importance Of A Healthy Liver
Just from these functions alone, it is clear the liver is the most important organ for detoxing the body. Because of this, keeping the liver healthy is in our best interest. Once heavy metals begin to accumulate in the liver, all sorts of problems arise. Some health problems you might experience once heavy metal accumulation occurs in the liver include:
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Fever
- Itchy skin and rashes
- Swelling in the extremities
Foods And Supplements That Support Liver Health For A Heavy Metal Cleanse
None of these are ideal, so liver health is vital to do a heavy metal cleanse. So how do we keep our liver healthy? I will list off several foods and supplements that work to support your liver so you can detox effectively.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #1: Green Tea
Tea is used across many cultures as a tool for healing. While tea is widely used and accepted as beneficial for your health, it is also beneficial for the liver. When I talk about tea here, I am talking about green tea. A study conducted on people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease showed improvement in liver enzyme production after a few months when regularly drinking green tea. As a word of caution, there has been some research suggesting green tea extract can cause liver damage in some people, so talk to a doctor before going heavy on it. However, for most people, a cup of green tea once a day is just fine.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #2: Berries
Berries make this list because not only are they delicious, but they are packed full of antioxidants. Antioxidants are important because of free radicals. Free radicals are created when heavy metals create oxidative stress. These free radicals can cause inflammation and other problems quickly. Antioxidants neutralize those free radicals and reduce inflammation. Some of the best berries to eat to boost your antioxidants include:
- Cranberries
- Strawberries
- Blueberries
- Elderberries
However, I want to highlight blueberries. The anthocyanins found in blueberries give them their deep color. Furthermore, there are studies showing a few weeks of blueberry and other berry juices not only boosts immune health but also protects the liver from damage and inflammation. Your liver needs antioxidants to protect itself from heavy metal damage. So, to do a heavy metal cleanse properly, supply your liver with berries for antioxidants.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #3: Beetroot/Beetroot Juice
Like berries, beetroots are also packed with antioxidants to protect the liver from free radical damage. One of the big perks of beetroot and beetroot juice is its nitrate content. Nitrates convert into nitric oxide within the endothelium of blood vessels. As this happens, nitric oxide gets released into the bloodstream. When this happens, your blood vessels expand, and blood flow becomes more efficient. This means oxygen and nutrients are transported faster throughout the body where they are needed. This means the good vitamins and minerals in the liver get transported to vital areas faster while heavy metals get excreted more effectively. Beetroot shows us that nitric oxide is a friend to your liver, so make sure you do what you can do to boost it during a heavy metal cleanse.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #4: Leafy Greens
It is easier to lump all these vegetables into a single category rather than write about them all individually. These include kale, arugula, spinach, mustard greens, lettuce, chard, and other leafy green vegetables. All these vegetables are packed full of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that keep your liver and the rest of your body healthy. Any natural heavy metal cleanse would include leafy greens.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #5: Fish
This one is tricky. Yes, some fish that are “good for you” also happen to be the ones most likely to contain mercury or lead. So, knowing the source of your fish is highly important here. However, despite the heavy metal contamination risk, fish is still good for you. We need the omega-3 fatty acids fish contains to reduce inflammation and liver fat accumulation. This means eating fish can help your liver perform better. Since the liver is responsible for detoxing our body, that is kind of important. Just make sure you check and verify the source of your fish. Pay close attention to where salmon, tuna, and swordfish come from.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #6: Olive Oil
Olive oil has research that supports its being able to improve fat levels and enzyme levels in the liver. Furthermore, olive oil also supports insulin sensitivity. Olive oil is a healthy source of good fats to add to your diet during or after a heavy metal cleanse to keep your liver healthy.
Heavy Metal Cleanser #7: Micronutrients
We know the liver produces, stores, and releases essential vitamins and minerals into the bloodstream. To get a better grip on specific micronutrients the liver needs to function, below you will find a list of some of the vitamins and minerals the liver needs to stay healthy.
- Selenium
- Iron
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- Magnesium
This list is not a complete list, but these are some of the most important vitamins and minerals needed for a healthy liver. Any heavy metal cleanse done medically or at home would need to include these vitamins and minerals to make sure the liver has what it needs to do its job.
Final Thoughts
Your liver is essential for your overall health and the most important organ for a heavy metal cleanse. You need to give it all the support you can to keep it healthy. All the foods and supplements listed above will help your liver function optimally. If you want to learn more about heavy metals or how to live a healthier life, check out the rest of our blog here.