The Comprehensive Guide to EDTA Chelation: Detoxifying Heavy Metals and Reducing Arterial Calcification

EDTA chelation therapy has been a subject of medical research and practice for several decades. Initially it was used for lead detoxification in the mid-20th century. Because of this, its application has expanded to address various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and heavy metal poisoning.
This article explores the history, mechanisms, and benefits of EDTA chelation therapy. It focuses on its role in detoxifying heavy metals and reducing arterial calcification, as well as its potential as an oral supplement.
Because of rampant contamination in our food, water and the air we breathe, understanding how to use EDTA is more important than ever!
History of EDTA Chelation
EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid) was first synthesized in the 1930s and gained prominence during World War II as a treatment for lead poisoning among factory workers. Its ability to bind with metal ions and form stable compounds made it an effective agent for removing heavy metals from the body.
After the war, researchers began investigating its potential in treating atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions.
Mechanism of Action
EDTA chelation therapy works by binding to heavy metals in the bloodstream, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium. It forms complexes that are then excreted in the urine. This process effectively reduces the body’s toxic metal burden. Beyond heavy metal detoxification, EDTA has been observed to have a decalcifying effect on arterial walls by removing calcium deposits, which are a key component of arterial plaque.
Detoxifying Heavy Metals
Heavy metals accumulate in the body from various sources, including environmental pollutants, occupational exposure, and contaminated food and water. These metals can disrupt biological processes and increase oxidative stress, leading to chronic diseases. EDTA chelation therapy has been shown to effectively reduce levels of these toxic metals, thereby mitigating their adverse health effects.
Reducing Arterial Calcification
Calcification in the arteries is a hallmark of atherosclerosis, which can lead to cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. By chelating calcium, EDTA helps reduce arterial plaque and improve blood flow. Clinical trials, including the TACT (Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy), have provided evidence supporting the cardiovascular benefits of EDTA chelation therapy.
EDTA as an Oral Supplement
While intravenous administration is the most common form of EDTA chelation therapy, oral EDTA supplements have also become available. Oral chelation offers a less invasive option, with studies suggesting its efficacy in heavy metal detoxification and cardiovascular health improvement. However, the absorption and effectiveness of oral EDTA can vary.
Potential Benefits and Considerations
Sexual Function: Improved blood flow as a result of reduced arterial calcification. This could potentially enhance sexual function, given the critical role of circulation in sexual health.
Overall Health: By reducing the body’s burden of heavy metals and improving cardiovascular health, EDTA chelation therapy may contribute to a greater sense of well-being and vitality.
Safety and Side Effects: EDTA chelation therapy is generally considered safe when performed under medical supervision. Potential side effects may include kidney damage and mineral deficiencies.
Conclusion
EDTA chelation therapy offers a multifaceted approach to improving health by detoxifying heavy metals and reducing arterial calcification. Its history, from treating lead poisoning to potentially enhancing sexual function and cardiovascular health, illustrates its versatility and therapeutic potential.
The Potato Diet - Is It Legit?
The potato diet has gained attention as a simple, short-term weight loss strategy. Essentially, it involves eating only potatoes for a certain period, typically three to five days. This diet emphasizes consuming plain, cooked potatoes without adding toppings or condiments that increase calorie intake. The diet capitalizes on the nutritional value of potatoes and starch, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It is also low in calories. Proponents argue it can help with weight loss, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation and reset your gut.
Is The Potato Diet Legit?
The potato diet capitalizes on the nutritional profile of potatoes, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and a particularly beneficial type of starch known as resistant starch. Resistant starch passes through the stomach and small intestine undigested. It then reaches the colon where it serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria. Because it feeds the bacteria it potentially helps by resetting and improving gut health. This process can lead to a more balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for overall health, digestion, and even immune function.
The diet’s restrictive nature can help re-calibrate taste preferences, reducing cravings for overly processed, sugary, and fatty foods. By limiting food choices to plain potatoes, individuals may find their desire for unhealthy foods diminishes over time. It aids in the development of healthier eating habits. The monotony of the diet could also lead to a more mindful approach to eating, as individuals become more attuned to their hunger cues and satiety signals, rather than eating out of boredom or for emotional reasons.
The potato diet’s focus on a single, whole food also simplifies eating decisions. This potentially makes it easier for individuals to stick to a diet plan without the need for complicated recipes or calorie counting. This simplicity can be a breath of fresh air for those who have struggled with more complex diet regimes. As individuals progress through the diet, they might notice an improvement in their digestion and a reduction in symptoms such as bloating, thanks to the gut-friendly effects of resistant starch.
Additionally, the diet encourages the intake of a food that is naturally low in calories yet high in volume, which can lead to a feeling of fullness and satisfaction after meals, potentially aiding in weight loss without the sensation of deprivation. This aspect, coupled with the diet’s potential to foster a healthier gut microbiome, makes the Potato Diet a fascinating approach to not only resetting one’s digestive system but also to laying the foundation for long-term healthy eating habits.
The Potato Diet is certainly unique in its approach, its potential benefits for gut health, alongside its simplicity and the possibility to reset dietary preferences away from unhealthy options, make it a compelling option for those looking to improve their overall health and well-being. By focusing on the humble potato, this diet offers a straightforward, nutritionally grounded method for individuals seeking to enhance their digestive health, recalibrate their taste buds, and embark on a journey towards healthier eating habits.
Key Features of the Potato Diet
-
- Simplicity: The diet is straightforward, requiring individuals to eat only potatoes.
- Duration: It’s designed for short-term adherence, usually around three to five days.
- Nutritional Content: Potatoes provide essential nutrients, including vitamin C, potassium, and dietary fiber.
- Caloric Restriction: The diet naturally limits calorie intake, which can lead to weight loss.
How It Works
Participants consume 2-3 pounds of potatoes daily, avoiding all other foods. The potatoes should be cooked without oil, butter, or any rich sauces. Seasonings are allowed, but they should be low in calories. The high fiber content in potatoes contributes to a feeling of fullness, potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
Benefits:
-
- May promote quick weight loss due to low calorie intake.
- High in certain nutrients that are essential for health.
- Simple and easy to follow.
Arginine While Fasting: Unlocking the Benefits
Unlocking the Benefits of Arginine While Fasting for Weight Loss and Enhanced Autophagy.
Fasting has emerged as a transformative approach to weight loss and improved health. This is done through its role in promoting autophagy. Autophagy is the body’s natural process of cleaning out damaged cells and regenerating new ones. As individuals seek to maximize the benefits of fasting, the role of amino, especially arginine, becomes important. Arginine is not just a buzzword but a concept worth a topic of keen interest exploring. Anyone looking to enhance their fasting results, particularly for weight loss and autophagy can benefit from this information.
Understanding Arginine Role
Arginine, a semi-essential amino acid, plays a critical role in various bodily functions. This includes the production of nitric oxide, which improves blood flow and nutrient delivery throughout the body. During fasting, arginine levels can become limited. Intriguingly, this may benefit the fasting process by pushing the body to turn to its internal energy reserves. This helps by accelerating weight loss and potentially enhancing the autophagy process.
Weight Loss and Arginine
Fasting triggers the body to search for alternative energy sources, typically turning to stored fats, which leads to weight loss. Arginine supplementation during fasting presents a paradox. It is beneficial for its health properties, its availability might reduce the body’s need to tap into these fat reserves. However, understanding the balance between supplementation and natural body processes is key. For those fasting with the goal of weight loss, the strategic use of arginine could potentially support metabolic health without significantly disrupting the fasting-induced metabolic shift.
Boosting Autophagy with Arginine
Autophagy, a vital cellular cleanup process, is one of the most sought-after benefits of fasting. It plays a crucial role in cell health, aging, and the prevention of diseases. The question arises: does arginine supplementation affect autophagy during fasting? While the direct impact of arginine on autophagy during fasting requires more research, it’s clear that maintaining a balance is essential. Properly timed arginine supplementation could support the body’s natural processes without hindering the autophagic benefits of fasting.
Arginine’s Potential Impact on Autophagy
- Nutrient Sensing and Autophagy: Fasting triggers autophagy by creating a nutrient scarcity, signaling the body to start cellular cleanup. Arginine supplementation during fasting could alter nutrient-sensing pathways, affecting autophagy.
- mTOR Pathway Activation: Arginine activates the mTOR pathway, which can inhibit autophagy by increasing protein synthesis. Fasting aims to reduce mTOR activity to boost autophagy, so arginine might counter this effect.
- Benefits versus Drawbacks: Although arginine offers health benefits, its supplementation during fasting periods requires careful consideration. Timing arginine intake correctly could manage its impact on autophagy.
Fasting and Arginine Supplementation Considerations
- Align Supplementation with Health Goals: Individuals should tailor their supplementation strategy to their health goals. Minimizing arginine during fasting may be wise for those focusing on autophagy.
- Time Supplementation Wisely: Taking arginine outside of fasting periods may allow individuals to enjoy its benefits without affecting autophagy.
- Seek Expert Advice: Consulting with healthcare or nutritional experts is crucial due to the complexity of fasting, autophagy, and amino acid supplementation.
Arginine supplementation offers various health benefits but may influence autophagy during fasting. For those aiming to enhance autophagy through fasting, considering the timing and amount of arginine supplementation is important. By understanding these biological mechanisms, individuals can make informed decisions to optimize their health outcomes, balancing the benefits of fasting and arginine supplementation.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Arginine During A Fast
- Timing is Key. Consider the timing of arginine supplementation to ensure it aligns with your fasting goals. For those focusing on weight loss and autophagy, taking arginine outside of the fasting window can offer the benefits. This is done without interfering in the fasting process.
- Monitor Your Progress. Keep track of your fasting outcomes and how supplements like arginine affect your weight loss and overall health. Adjustments can always be made to optimize results.
- Balance Your Diet. During your eating windows, focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support your body’s needs. Including natural sources of arginine, such as nuts, seeds, and legumes is key.
To Summarize
Arginine during a fast is a nuanced topic with the potential to enhance the fasting experience, particularly for individuals focused on weight loss and autophagy. By understanding and respecting the delicate balance between supplementation and the natural fasting process, it’s possible to achieve optimal health outcomes.
Whether you’re a seasoned faster or just beginning your journey, the integration of arginine into your regimen requires thoughtful consideration to truly unlock the benefits of fasting.
Types Of Arginine And Health Benefits
The Types Of Arginine are important to know because each type can offer slightly different benefits. Lets dive deeper and find out why.
L-Arginine plays a pivotal role in numerous physiological processes, offering various health benefits. It supports blood pressure, circulation, and offers many health benefits.
Its different forms cater to specific needs, so some enhance its overall effectiveness and some its bioavailability. Let’s delve into the details of each type and how they are made.
L-Arginine HCl (Hydrochloride)
L-Arginine HCl (Hydrochloride) is a variant of the amino acid L-Arginine. It is crucial for several bodily functions. The list is large, including protein synthesis, ammonia detoxification, and the production of nitric oxide. The key difference between L-Arginine HCl and regular L-Arginine lies in their composition and solubility.
Differences from Base Arginine
- Composition: L-Arginine HCl combines L-Arginine with a hydrochloride molecule. This addition helps to stabilize the arginine, making it more palatable and increasing its solubility in water.
- Solubility: The primary advantage of L-Arginine HCl over base arginine is its enhanced solubility. This feature makes it easier to consume in liquid form and potentially improves its absorption in the digestive system.
- Taste: The hydrochloride form is generally considered to have a more tolerable taste comparing it to the base form, which is quite bitter.
Uses and Preferences
L-Arginine HCl is known for its various uses, particularly in areas related to cardiovascular health, athletic performance, and recovery from injuries or surgeries:
- Cardiovascular Health: Due to its role in nitric oxide production, L-Arginine HCl is often used to support cardiovascular functions. This includes improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
- Athletic Performance: Athletes may prefer L-Arginine HCl. It has strong potential for improving blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles during intense workouts. It is good for enhancing performance and recovery.
- Wound Healing: Its ability to improve circulation also makes L-Arginine HCl a candidate for supporting faster wound healing.
Choosing L-Arginine HCl over Other Forms
The choice between L-Arginine HCl and other forms of L-Arginine often depends on the specific needs and preferences. Also important are potential sensitivities people may have:
- Digestibility and Absorption: Those who might have sensitivity to the base form or require a more easily absorbed variant may opt for L-Arginine HCl due to its enhanced solubility.
- Specific Health Goals: L-Arginine HCl might be preferred for cardiovascular support or to enhance exercise performance, where rapid absorption and efficacy are desired.
- Taste Preferences: The less bitter taste of L-Arginine HCl can make it a more palatable option for individuals who struggle with the taste of base L-Arginine supplements.
In summary, while all forms of L-Arginine provide similar fundamental benefits due to their role in nitric oxide production and protein synthesis, the choice of L-Arginine HCl over others might be influenced by its solubility, absorption rate, taste, and specific health objectives. Always consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen is advisable to ensure it aligns with your health needs and goals.
L-Arginine AKG (Alpha-Ketoglutarate)
Arginine AKG (Alpha-Ketoglutarate) combines the amino acid L-Arginine with Alpha-Ketoglutarate, a crucial molecule in the Krebs cycle, responsible for energy production. This blend offers unique benefits over base L-Arginine and other Arginine forms.
Differences from Base Arginine
- Composition: The key difference lies in Alpha-Ketoglutarate’s addition to L-Arginine, enhancing the compound’s role in amino acid synthesis and energy generation.
- Absorption and Effectiveness: The body absorbs and utilizes L-Arginine AKG more efficiently than base L-Arginine. Alpha-Ketoglutarate increases L-Arginine’s stability and bioavailability.
- Energy Production: L-Arginine AKG’s involvement in the Krebs cycle makes it highly effective in boosting energy, offering significant benefits for energy-demanding activities.
Uses and Preferences
L-Arginine AKG is particularly popular for specific uses, mainly in the realms of athletic performance and recovery:
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Athletes and bodybuilders often choose L-Arginine AKG for its superior ability to boost nitric oxide production, enhancing blood flow, oxygen delivery to muscles, and overall performance.
- Supports Muscle Recovery: The compound aids in quicker muscle recovery post-intense workouts by improving nutrient delivery to muscles.
- Energy Boost: People looking for an energy increase during physical activities benefit from L-Arginine AKG, thanks to its critical role in the energy production cycle.
Choosing L-Arginine AKG over Other Forms
Choosing L-Arginine AKG over other Arginine forms usually aligns with specific goals, especially concerning physical performance and energy needs:
- For Athletic Performance and Recovery: Individuals aiming to maximize physical performance and enhance muscle recovery might find L-Arginine AKG more suitable due to its nitric oxide production and absorption benefits.
- For Energy Enhancement: Those in need of an energy uplift for workouts or athletic endeavors may prefer L-Arginine AKG for its direct involvement in energy production.
L-Arginine Aspartate
Arginine Aspartate stands out from L-Arginine AKG and base L-Arginine due to its unique combination and specific applications:
Unique Characteristics of L-Arginine Aspartate
- Aspartate Component: Unlike AKG, which is involved in the Krebs cycle and energy production, aspartate plays a critical role in the urea cycle. It is adept at helping to eliminate excess nitrogen from the body. This function of aspartate can enhance endurance by efficiently removing ammonia. Ammonia is a byproduct of exercising muscle, thus potentially reducing fatigue.
- Neurotransmitter Support: Aspartic acid acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain. This can influence the production of testosterone, enhancing hormone levels that are crucial for muscle mass and strength. This aspect differentiates it from L-Arginine AKG, which does not directly influence neurotransmitter levels or hormone production.
- Enhanced Endurance and Recovery: Both AKG and aspartate forms are known for their potential to enhance athletic performance,. L-Arginine Aspartate however, specifically offers benefits related to endurance and recovery. This is due to its role in ammonia detoxification.
Applications and When to Use L-Arginine Aspartate
- For Enhanced Endurance Sports Performance: Due to its efficient role in ammonia detoxification, individuals engaged in endurance sports might prefer L-Arginine Aspartate to support longer periods of physical activity and to reduce recovery time.
- When Seeking Hormonal Support: Those looking into natural ways to support hormone production, particularly testosterone, might find L-Arginine Aspartate beneficial due to the neurotransmitter role of aspartic acid.
- For Comprehensive Athletic Support: Athletes focusing on both performance and recovery, especially in sports that demand high endurance, might choose L-Arginine Aspartate over AKG or base L-Arginine for its dual action in energy metabolism and detoxification.
In contrast to L-Arginine AKG, which is often chosen for its direct benefits on energy production and nitric oxide synthesis, L-Arginine Aspartate offers a broader spectrum of support, particularly beneficial for endurance and recovery, making it a distinct choice for athletes and individuals seeking specific health benefits.
L-Arginine Malate
Arginine Malate is a compound that combines L-Arginine with Malate, a tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle or Krebs cycle) intermediate. This combination offers distinct advantages and uses compared to other forms of L-Arginine.
Differences and Unique Benefits of L-Arginine Malate
- Enhanced Energy Production: Malate plays a crucial role in the Krebs cycle, a key energy-producing process in the body. L-Arginine Malate, therefore, not only boosts nitric oxide levels but also supports energy production at a cellular level. Therefore making it particularly beneficial for endurance and performance.
- Improved Athletic Performance: Due to its dual role in enhancing nitric oxide production and supporting the Krebs cycle, L-Arginine Malate is often chosen by athletes. They choose it seeking to improve their performance, endurance, and recovery times.
- Support for Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism: The presence of Malate supports both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without oxygen) energy pathways, offering a versatile energy boost that can be beneficial across different types of physical activities.
Contrast with Other Forms of L-Arginine
- L-Arginine HCl: While L-Arginine HCl is primarily sought after for its improved solubility and absorption, L-Arginine Malate offers the added benefit of supporting energy production, making it a more suitable choice for individuals looking to enhance physical performance and energy levels.
- L-Arginine AKG: Although L-Arginine AKG is also known for its role in energy production and nitric oxide synthesis, L-Arginine Malate might be preferred for activities that require sustained energy over longer periods, due to the efficient role of Malate in the Krebs cycle.
- Base L-Arginine: The base form of L-Arginine primarily serves to increase nitric oxide production. However, L-Arginine Malate extends beyond this by also enhancing energy production, offering a broader range of benefits for physical activity and performance.
When to Use L-Arginine Malate
- Endurance Athletes: Individuals engaged in long-duration sports or activities may find L-Arginine Malate particularly beneficial for its dual role in boosting nitric oxide levels and supporting sustained energy production.
- Those Seeking Enhanced Recovery: The improved blood flow from increased nitric oxide production, combined with efficient energy metabolism, can help facilitate quicker recovery after intense workouts.
- Individuals Focused on Aerobic and Anaerobic Performance: L-Arginine Malate’s support for both energy pathways makes it an excellent choice for athletes who engage in a mix of aerobic and anaerobic exercises.
In summary, L-Arginine Malate offers unique benefits that make it stand out from other forms of L-Arginine, especially for athletes and individuals seeking to improve their energy levels, performance, and recovery. Its ability to support nitric oxide production and energy metabolism simultaneously provides a comprehensive approach to enhancing physical performance.
In essence, L-Arginine AKG stands out for individuals focused on sports performance. It’s great for recovery, and energy thanks to its enhanced bioavailability and contribution to energy metabolism. Each of these forms of L-Arginine is designed to optimize the amino acid’s benefits. Whether used for improving cardiovascular health, enhancing athletic performance, or supporting overall well-being. The choice of form can depend on the desired effect, the method of delivery, and individual tolerance.
Heavy Metal Detox Kit
Heavy Metal Detox Kit: Unveil the Power with Chelanox
In the modern environment, heavy metals infiltrate our bodies from sources like pollution, food, and water. These toxins can accumulate so they pose grave health risks. The heavy metal detox kit in capsule for “Chelanox” presents a comprehensive solution. This is because it combines natural ingredients, each selected for their detoxifying properties. Let’s delve into the ingredients that make Chelanox a potent choice for purging heavy metals from the body.
Chelanox Ingredients for Effective Heavy Metal Detox
EDTA: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) acts as a chelating agent, binding to heavy metals in the bloodstream to facilitate their removal. It efficiently targets metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic, so we have made it a cornerstone of detox efforts.
EDTA Safety
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is generally safe when used under medical supervision. It’s commonly used in chelation therapy to remove heavy metals from the bloodstream. However, it’s essential to use it correctly, as inappropriate doses can lead to adverse effects.
Chlorella Algae Safety
Chlorella Algae is considered safe for most people when consumed in recommended amounts. It’s rich in nutrients and has been used in supplements for detoxification. People with allergies to molds or a sensitivity to iodine should exercise caution.
Chlorella Algae: This green algae binds to heavy metals, aiding in their removal. Its high chlorophyll content boosts detoxification, making it a key ingredient in Chelanox.
Modified Citrus Pectin: Easily absorbed by the body, this form of pectin chelates heavy metals, supporting their excretion. It also enhances cellular health and immune function, offering benefits beyond detoxification.
Modified Citrus Pectin Safety
Modified Citrus Pectin is safe for most individuals when taken orally. It is derived from citrus peels and has been used in dietary supplements for its detoxifying properties. As with any supplement, following recommended doses is crucial to avoid digestive discomfort.
Cilantro Leaf Extract 4:1: Celebrated for its detoxifying capabilities, especially in mercury removal, cilantro’s concentrated extract amplifies these benefits in Chelanox.
Cilantro Leaf Extract Safety
This leaf is generally safe when consumed in food amounts. The extract is used for detoxification purposes. It should be taken according to product guidelines to avoid any potential side effects, such as allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Shilajit 10:1 Extract: Packed with fulvic acid, Shilajit boosts the body’s detox pathways, supporting toxin removal. Its inclusion enhances Chelanox’s effectiveness against heavy metal accumulation.
Shilajit Safety
This is a natural resin, is considered safe for most adults when taken in supplement form at recommended dosages. It’s important to source Shilajit from reputable suppliers, as low-quality products may contain harmful contaminants.
Zeolite: This mineral traps and removes heavy metals, thanks to its unique structure. It’s an excellent addition to Chelanox, contributing to its detox prowess.
Zeolite Safety
Zeolite supplements are safe for short-term use. Limited data exists on their long-term safety, so using zeolite with a healthcare provider’s guidance, especially for detox purposes, is advisable.
NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine): As a precursor to glutathione, a potent detoxifier, NAC combats oxidative stress and aids the liver in eliminating heavy metals.
Alpha Lipoic Acid: This antioxidant aids the body’s detox processes because it rejuvenates other antioxidants, bolstering the fight against heavy metals.
Uva Ursi Leaf Powder: Supporting urinary tract health, Uva Ursi facilitates toxin elimination, including heavy metals, through the urinary system.
Milk Thistle Seed Powder: This herb enhances liver health so it is crucial for detoxification. It protects and regenerates liver cells, improving the body’s capacity to cleanse itself of toxins, including heavy metals.
Conclusion
Chelanox’s heavy metal detox kit excels with its blend of natural ingredients, each playing a role in the effective removal of heavy metals. Every element of Chelanox has designed to enhance detoxification and works in promoting health. Choosing Chelanox allows individuals to cleanse their bodies naturally and support overall well-being effectively.
Arginine and PAD
Arginine and PAD: A Comprehensive Overview
Arginine, an essential amino acid, plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions. The most well known role is in the regulation of blood pressure. Historically, researchers have studied its benefits, particularly those related to improving cardiovascular health.
Arginine’s works because of the synthesis of nitric oxide, a compound essential for opening your blood vessels, thereby reducing blood pressure. Studies, such as those published in the “Journal of Clinical Hypertension,” highlight its efficacy in managing hypertension, a common precursor to Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD).
The Connection Between Arginine and PAD
Peripheral Arterial Disease is a condition where one has a narrowing of blood vessels and reduced blood flow. This is usually in the legs. The link between arginine and PAD stems from arginine’s ability to improve blood flow.
By enhancing nitric oxide production, arginine aids in dilating blood vessels, which is crucial for PAD patients. Research in the “American Heart Journal” supports the use of arginine supplementation, showing significant improvement in the symptoms of PAD, such as leg pain and walking distance.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Arginine for PAD
Clinical trials further make the case for arginine’s role in PAD management. A landmark study published in “Circulation” demonstrated that arginine supplementation led to marked improvements in endothelial function among PAD patients.
Participants reported enhanced walking ability and reduced symptoms, underscoring arginine’s potential as a therapeutic agent. Another study in the “European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing” echoed these findings, noting improved quality of life in PAD patients following arginine supplementation.
The Future of Arginine in PAD Treatment
The growing body of evidence suggests a promising future for arginine in PAD treatment. As research continues to evolve, arginine’s role becomes increasingly significant. Healthcare professionals are beginning to recognize the amino acid’s value not only in managing PAD symptoms but also in offering a non-invasive treatment alternative. With further studies ahead for sure, arginine could become a cornerstone in PAD therapy, offering hope to those afflicted by this debilitating condition.
Arginine’s journey from a blood pressure regulator to a potential PAD treatment highlights its therapeutic powers. The amino acid’s ability to enhance nitric oxide production and improve vascular function positions it as an invaluable tool in combating PAD. Arginine stands out as a beacon of hope for millions suffering from cardiovascular diseases. It’s use promises a healthier, more active future for many.
How Can I Tell if Taking Arginine is Helping?
Determining the effectiveness of Arginine, especially for conditions like Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), involves observing specific health improvements. Consulting with healthcare professionals is also key. Here are a few things to watch for:
- Improved Circulation and Reduced Symptoms of PAD: Arginine can enhance blood flow, leading to noticeable improvements in symptoms associated with PAD. These can be things such as less pain during walking, increased walking distance without discomfort, and reduced symptoms of leg pain due to poor circulation.
- Enhanced Exercise Performance: As Arginine helps improve blood flow, you might find an improvement in your overall exercise habbits. This includes longer times of physical activity without fatigue and better recovery.
- Blood Pressure Changes: Arginine’s impact on nitric oxide production can lead to vasodilation. This is just a fancy way of saying “It opens your veins”. This helps in reducing blood pressure. Monitoring your blood pressure can provide tangible evidence of Arginine’s effects. A consistent decrease in readings may indicate its positive impact on your cardiovascular health.
- Consult Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal changes in the levels of certain markers that indicate improved vascular health. One important one is reduced levels of LDL cholesterol and increased HDL cholesterol. Your doctor can help interpret these results and determine if Arginine is contributing to these changes.
- Professional Evaluation: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are vital. They can perform tests to assess the health of your blood vessels and heart, providing a professional perspective on whether Arginine is beneficial for you.
Remember, while these indicators can suggest Arginine’s effectiveness, individual responses may vary. It’s essential to use Arginine under medical supervision. Especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications. Always discuss with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it’s appropriate for your health needs.
Join Us To Learn More
Joining the Bionox newsletter and trying Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition could be a game-changer for your health. This is especially true if you’re seeking to improve cardiovascular wellness and enhance overall vitality.
By subscribing below, you’ll gain exclusive access to the latest insights, health tips, and breakthroughs in nitric oxide research and nutrition. Ultimate Nitric Oxide Nutrition, crafted with precision, aims to harness the power of Arginine and other key nutrients to support optimal blood flow, energy levels, and nutrient delivery throughout your body.
This innovative approach not only targets the foundations of cardiovascular health but also empowers your body to perform at its best. Whether you’re looking to boost your exercise performance, improve circulation, Bionox offers the knowledge and nutritional solutions to guide you on your journey. Join the Bionox community today to start transforming your health with the power of nitric oxide nutrition.
6 Juices to Naturally Detox from Heavy Metals
Naturally Detox from Heavy Metals
Heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, and arsenic, can accumulate in our bodies over time. This can lead to a range of health issues. From cognitive problems to digestive disturbances, the impacts of heavy metal toxicity can be profound. Fortunately, certain dietary choices, including specific juices, can aid in the detoxification process. Juicing can help to cleanse your body of these harmful substances so it’s important to learn about them. This article explores six potent juices you can use and benefit from. These juices are not always delicious but they can play a crucial role in detoxifying the body from heavy metals.
Understanding Heavy Metal Toxicity
Heavy metals naturally occur in the environment, but excessive exposure can lead to accumulation in our bodies. This can pose significant health risks. These metals can enter our system through contaminated food, water, industrial exposure, and even beauty products. This accumulation can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and more serious conditions like kidney dysfunction and neurological disorders.
The Role of Diet in Detoxification
Diet plays a pivotal role in supporting our body’s natural detoxification processes. Certain nutrients and foods can help you to naturally detox from heavy metals, with specific juices standing out for their detoxifying properties. These juices are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and compounds that support liver function. They also aid in the chelation process (binding and removing metals), and bolster the immune system.
Juices for Heavy Metal Detox
Here’s a list of known juices that can aid in the removal of heavy metals. Each is accompanied by a brief overview of their benefits:
- Cilantro Juice: Cilantro is renowned for its chelating abilities, helping to bind heavy metals and facilitate their elimination from the body. A simple blend of fresh cilantro leaves with water can create a powerful detox juice.
- Wild Blueberry Juice: Wild blueberries are packed with antioxidants that support the detoxification process. This is particularly useful in cleansing the brain and liver.
- Chlorella Green Juice: Chlorella, a type of algae, is a potent detoxifier known for its ability to bind to heavy metals.
- Spirulina Drink: Spirulina is another algae with strong chelating properties, making it effective in heavy metal detoxification.
- Ginger and Lemon Juice: This combination not only boosts digestion but also supports liver function an essential organ.
- Beetroot and Apple Juice: Beetroot and apple both support liver health and detoxification, with beetroot particularly known for its blood-cleansing properties.
The Best Juices To Detox
Cilantro Juice
Benefits: Cilantro is a powerful herb for detoxing so we mention it first. It binds to heavy metals, aiding their removal from the body. This makes it a top choice for detox juices. Like a lot of the juices mentioned below, you probably do not want to juice it alone. It’s probably best to mix it with one of the other juices mentioned below!
Wild Blueberry Juice
Benefits: Wild blueberries are antioxidant-rich. They support the body in removing heavy metals, especially from the brain. They are delicious so try mixing them with the other plants mentioned here to make it all taste good!
Tips:
- Use fresh or frozen wild blueberries.
- Blend with a bit of water for a pure juice.
- Drink daily for best results.
Chlorella Green Juice
Benefits: Chlorella is a green algae with a high capacity for detoxification and it’s amazing! It binds to metals, facilitating their expulsion.
Spirulina Drink
Benefits: Spirulina, another algae, is effective in cleansing the body of heavy metals. It’s nutrient-dense and supports overall health therefore it is great for you.
Ginger and Lemon Juice
Benefits: Ginger and lemon boost digestion and liver function. They help the liver process and eliminate toxins, including heavy metals.
Beetroot and Apple Juice
Benefits: Beetroot and apple support liver health and blood purification. They’re effective in helping the body detox from heavy metals.
The Best Natural Heavy Metal Detox Supplement
Chelanox by Bionox stands out as a superior alternative to juicing for detoxification, because of its ease of use and potent formula. Unlike the time-consuming process of selecting, washing, and juicing fruits and vegetables, Chelanox is a no-fuss approach to detoxing.
Meticulous Formulation
It is meticulously formulated with a blend of ingredients known for their detoxifying properties. It provides a concentrated dose of nutrients that support the body’s natural detox processes. This makes Chelanox not only more convenient than juicing but also potentially more effective, and it is designed to target heavy metals directly and facilitate their removal.
Easier Than Juicing
For those seeking a reliable, efficient way to cleanse their body of toxins, Chelanox represents a hassle-free, potent solution, eliminating the need for extensive preparation and cleanup associated with juicing.

Chelanox sets itself apart as a superior detoxification solution, especially when compared to traditional juicing methods. This superiority stems from its carefully selected, powerful ingredients designed to efficiently cleanse the body of heavy metals. Each component in Chelanox plays a crucial role:
- EDTA: Known for its chelating properties because it binds to heavy metals, facilitating their removal from the body.
- Chlorella Algae: A superfood that supports detox by binding to toxins and promoting their elimination.
- Modified Citrus Pectin: Has the unique ability to cross the intestinal barrier, so it aids in the detoxification process.
- Cilantro Leaf Extract: Acts as a natural chelator, assisting in the removal of heavy metals from the body.
- Shilajit Extract: Enhances the body’s natural detoxification process and supports overall vitality.
- Zeolite: A natural mineral that traps heavy metals and toxins, allowing them to be safely excreted from the body.
- Glutathione Precursor Support Blend: Supports the production of glutathione, a critical antioxidant for detoxification.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid: Helps to protect the body from oxidative stress and supports the detoxification of heavy metals.
- Uva Ursi Leaf Powder: Supports urinary tract health, which is crucial for the elimination of toxins.
- Milk Thistle Seed Powder: Promotes liver health and its ability to process and eliminate toxins.
The comprehensive formula of Chelanox not only targets heavy metals for removal but also supports the body’s natural detoxification systems, making it a more effective and easier alternative to juicing. Unlike juicing, which requires daily preparation and consumption of large quantities of fruits and vegetables, Chelanox provides a simple, efficient, and direct approach to detoxification. With just a few capsules, users can achieve a level of detox that might require multiple glasses of juice, saving time and effort without compromising on the effectiveness of the detox process.
Top 5 Reasons to Stop Taking Arginine Alone
Stop Taking Arginine you say? Is there a reason you should stop or is there simply a better way to take it? Lets see!
Scientists discovered arginine, an amino acid, in the late 19th century. Its use has surged in popularity over the years as a coveted supplement among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. It is also popular amoung those seeking to improve their cardiovascular health. Also, it can support lower blood pressure and offers support for those seeking cognitive improvements.
What Is Arginine?
This semi-essential amino acid plays a pivotal role in synthesizing proteins and supporting nitric oxide production in the body. It also enhances blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscle tissues. Its reputation for boosting exercise performance, aiding in recovery, and offering cardiovascular benefits is well know. This reputation has cemented arginine’s place on the shelves of health stores and in the regimens of health-conscious individuals worldwide. But does it work? Should you stop taking arginine?
The burgeoning interest in arginine has also ushered in a wave of scrutiny and research aimed at understanding its efficacy.
Arginine’s Benefits
Arginine’s benefits are not in dispute. Emerging evidence, however, suggests that its effectiveness can be significantly amplified when combined with other nutrients. So and we aim to show why your should stop taking arginine alone. This article aims to shed light on the limitations of solo arginine supplementation. We strongly advocate for its combination with other nutrients because of improved health outcomes.
One of the primary reasons behind the push for combining arginine with other ingredients lies in its bioavailability. The body’s ability to utilize it effectively is a common concern. It also has a powerful effect of other substances such as NOS ( Nitric Oxide Synthase). When taken alone, the absorption of arginine can encounter physiological barriers that limit its effectiveness, absorption and lifespan.
Other Amino Acids
The presence of other amino acids can compete with arginine for absorption in the gut. This reduces the amount that ultimately enters the bloodstream and reaches the tissues where it is most needed. However, some amino acids have the opposite effect and can boost its effect! Just this alone is a great justification for why you should stop taking arginine alone!
This competition from the wrong kinds of amino acids can diminish the perceived benefits of arginine. This is particularly so in the realms of exercise performance and cardiovascular health.
Better Blood Vessel Dilation
Arginine’s role in the production of nitric oxide has been well-documented. This is because the conversion of arginine into nitric oxide can be inefficient without other complementary nutrients. This inefficiency highlights another limitation of relying solely on arginine. To achieve desired health outcomes, such as improved blood flow and improved exercise capacity, more is needed.
The case for combining arginine with other nutrients also extends to its synergistic interactions with certain vitamins and minerals. For example, vitamin D has been shown to work in tandem with arginine to bolster the immune system. It also plays a role in helping to support bone health. Antioxidants like vitamins E and C can enhance arginine’s cardiovascular benefits by reducing stress and inflammation. These interactions underscore the multifaceted nature of nutrition and wellness. This is because the combined effect of different nutrients often surpasses the sum of their individual benefits.
Arginine As A Supplement
The purpose of this article is not to diminish the value of arginine as a supplement. We aim to illuminate a more nature based approach to its use. By combining arginine with complementary nutrients such as citrulline, vitamin D, horse chestnut, and vitamins E and C, individuals can potentially unlock a broader spectrum of health benefits and achieve more pronounced improvements in cardiovascular health, exercise performance, and overall well-being.
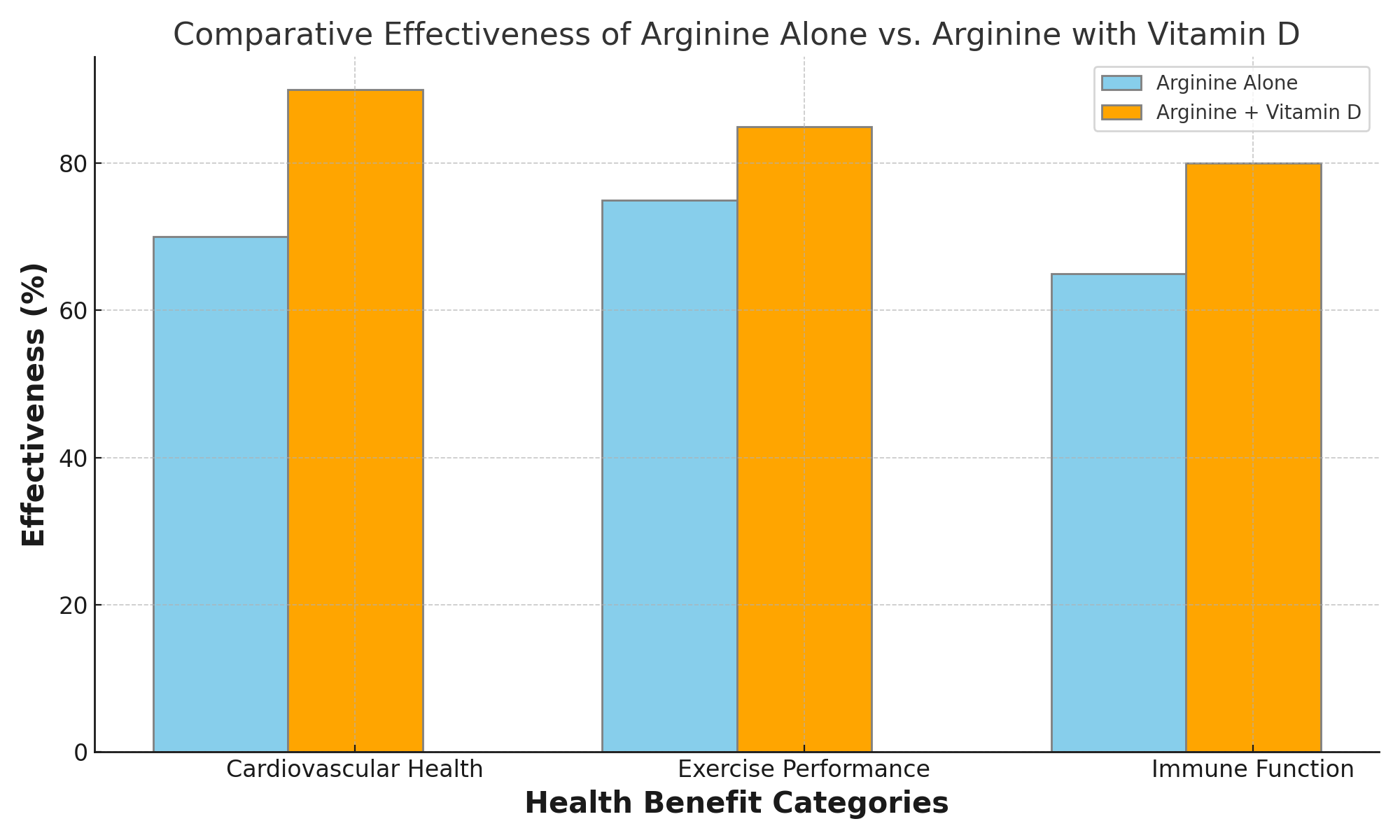
As we delve deeper into the limitations of solo arginine supplementation it becomes clear that the path to optimal health is not through isolated ingredients. We see it is through a well-rounded and informed approach to nutrition. This perspective enriches our understanding of how different nutrients interact. It also empowers us to make more effective decisions about our health and wellness strategies.
Reason 1: Limited Absorption and Bioavailability
Arginine, when consumed as a standalone supplement, faces significant challenges related to its absorption and bioavailability in the human body. This amino acid competes with other amino acids for transporters in the gut and bloodstream. This competition can significantly reduce the amount of arginine that is effectively absorbed and utilized by the body. Yet another reason why you should stop taking arginine alone.
Absorption
The presence of other amino acids in the digestive system can inhibit arginine’s entry into the bloodstream. This sometimes diminishes its overall effectiveness, making it a waste of time and money to consume.
The bioavailability of arginine is not just about how much is absorbed. How efficiently it is used by the body is also important. This is because once absorbed, arginine serves as a precursor for the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO). As mentioned before NO a critical molecule for cardiovascular health, immune function, and wound healing.
The conversion rate of arginine to nitric oxide can be lowered or just plan stopped in the absence of complementary nutrients. This leads to less than ideal health outcomes. So to summarize, add the wrong things and arginine may not work. Add the right things and you can put it in overdrive!
Combinations That Count: Stop Taking Arginine By Itself
The issue of limited absorption and bioavailability underscores the importance of not just consuming arginine but ensuring it is taken correctly. This can be improved by combining arginine with other things that enhance its absorption or work together to bolster its effects.
For instance, pairing arginine with citrulline, another amino acid, has been shown to enhance the overall bioavailability of arginine, see chart below for more info.
Citrulline is converted into arginine in the kidney, which not only increases the plasma levels of arginine but also prolongs its availability for nitric oxide production, thereby amplifying the cardiovascular benefits.
Summary of Reason #1
So in summary, while arginine alone possesses undeniable health benefits, its limited absorption and bioavailability can hinder its effectiveness. There are great reasons why you may want to stop taking arginine alone. By understanding and addressing these limitations through strategic supplementation, individuals can better harness arginine’s potential health benefits. This approach not only optimizes the intake of arginine but also underscores a broader principle. That being; nutritional supplementation often yields the best results when approached naturally.
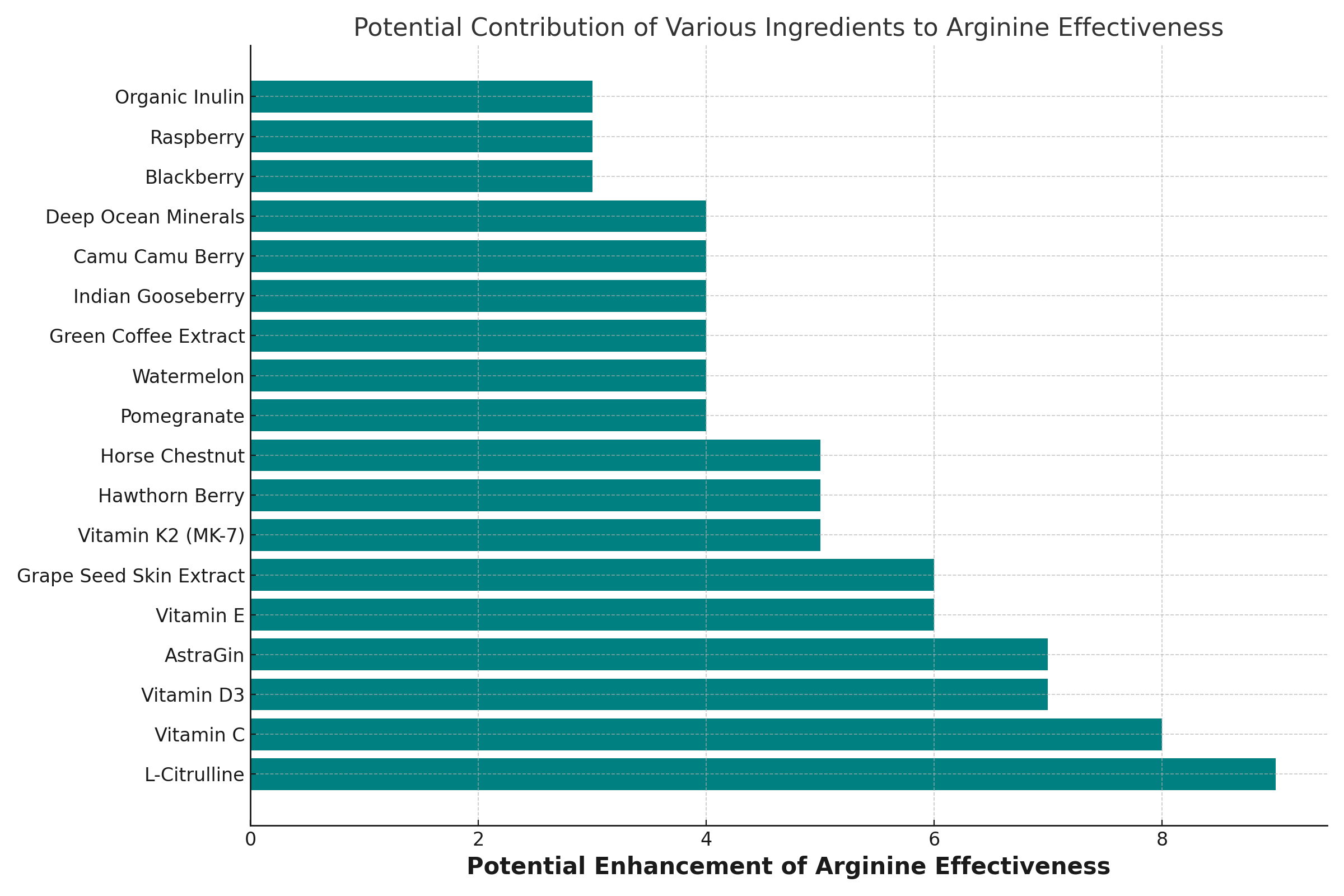
Stop Taking Arginine Alone
- Vitamin C: Enhances nitric oxide production from Arginine by stabilizing it and reducing its breakdown.
- Vitamin D3: Works synergistically to support cardiovascular health and may enhance the effectiveness of Arginine. Vitamin D also helps your body produce more NOS.
- Vitamin E: Protects cells from cellular stress, potentially enhancing Arginine’s effects on vascular health.
- Vitamin K2 (MK-7): May work with Arginine to support arterial health and flexibility.
- L-Citrulline: Converts to Arginine in the body, increasing Arginine levels and nitric oxide production.
- Pomegranate, Watermelon, Blackberry, Raspberry: These fruits are rich in antioxidants and other compounds that can support nitric oxide production and enhance the effects of Arginine.
- Hawthorn Berry, Horse Chestnut: Known for their vascular health benefits, potentially complementing Arginine’s cardiovascular effects.
- Green Coffee Extract, Indian Gooseberry, Grape Seed Skin Extract, Camu Camu Berry: These ingredients offer antioxidant support, which can synergize with Arginine’s health benefits.
- Deep Ocean Minerals: May provide trace minerals that support overall metabolic processes, including those involving Arginine.
- AstraGin: Known to enhance nutrient absorption, potentially improving Arginine bioavailability.
- Organic Inulin: A prebiotic fiber that can support gut health, possibly affecting Arginine’s absorption positively.
Cardiovascular Health
Arginine is well-known for its critical role in the production of nitric oxide (NO). NO is a vital molecule that influences various aspects of cardiovascular health as we have discussed above.
Nitric oxide acts as a vasodilator, meaning it relaxes the inner muscles of blood vessels. This causes them to widen and thereby improve blood flow and energy, etc.
This effect can lower blood pressure, enhance exercise performance, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It even helps with some cognitive issues and diseases of the eye as well.
Despite its potential, the production of nitric oxide from arginine can be hampered when arginine is consumed alone. This is due to factors like enzyme availability, oxidative stress, and the presence of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA). ADMA is a natural inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis. In other words, if you stop taking arginine by itself, you get more of it. The results are better if your taking it with the right things.
Citrulline
The combination of arginine with citrulline is a strategy that can overcome these limitations. Combining the two can lead to more efficient nitric oxide production. This is yet another reason why you may want to top taking arginine alone. Citrulline is converted into arginine in the kidneys. It increases the plasma levels of arginine and also provides a more sustained release of arginine for nitric oxide production. Combining bypasses the competitive absorption issues in the gut. It also helps maintain higher levels of nitric oxide in the bloodstream. Combining the two enhanci cardiovascular benefits such as improved vascular tone, blood flow, and reduced blood pressure.
Vitamins E, C, and K2
These play supportive roles in enhancing nitric oxide production and ensuring its stability:
Vitamin E
This antioxidant helps protect nitric oxide from degradation via oxidatiion that can rapidly neutralize nitric oxide. It reduces the availability and effectiveness of NO in vasodilation. By reducing oxidative stress, vitamin E preserves nitric oxide levels. More NO means more cardiovascular benefits.

Vitamin C
Similar to vitamin E, vitamin C is an antioxidant that can synergize with arginine by stabilizing nitric oxide. Vitamin C reduces its breakdown in the bloodstream. C has also been shown to regenerate vitamin E, thus working together. These vitamins create a powerful antioxidant network that protects nitric oxide and enhances its effects on blood vessel dilation.

Vitamin K2 (MK-7)
While its role in nitric oxide production may not be as apparent as other vitamins, vitamin K2 contributes to cardiovascular health. It does so by preventing calcium deposition in the arteries. This action helps maintain arterial flexibility and function. There is emerging evidence that vitamin K2 may also support the endothelial function. This is is crucial for nitric oxide production and regulation. By promoting overall vascular health, vitamin K2 can indirectly support the optimal function of nitric oxide.

So, while arginine is a key precursor to nitric oxide its solo use can result in poor nitric oxide production. This is due to various physiological constraints, making it kind of a waste of money to take alone.
Combining arginine with citrulline and other vitamins can significantly enhance the production of nitric oxide. This strategic supplementation approach not only amplifies the cardiovascular benefits. It also supports broader health outcomes and benefits. This is done by ensuring efficient blood flow and nutrient delivery throughout the body and therefore more nitric oxide.
Reason 3: Inadequate Support for Vascular Health
Vascular health is fundamental to the overall well-being of the cardiovascular system, brain, gut, you name it. Healthy blood vessels are essential for the efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients to every part of the body. They also are vital for the removal of waste products, energy, vitality and pretty much everything.
Good vascular health also plays a critical role in preventing conditions such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and PAD to name a few. While arginine is renowned for its capacity to enhance nitric oxide production and thus improve vasodilation and blood flow, relying on arginine alone might not offer comprehensive support for vascular health. This is because vascular health encompasses more than just the ability of blood vessels to dilate; it also includes the strength, elasticity, and integrity of the blood vessel walls.
Horse Chestnut
Enter the synergistic potential of combining arginine with horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum), an herbal supplement known for its heart healthy properties. Horse chestnut can significantly enhance heart health. This amazing plant contains a compound called aescin. The active ingredients in aescin have been shown to strengthen capillary walls, reduce inflammation, and improve blood vessel tone. This can be particularly beneficial in conditions such as chronic venous insufficiency, where veins struggle to return blood to the heart efficiently.

The combination of arginine and horse chestnut works on multiple fronts to support vascular health. This is because of arginine’s role in nitric oxide production addresses the need for vasodilation and improved blood flow. Horse chestnut’s heart healthy and anti-inflammatory effects contribute to the structural health and functionality of the blood vessels.
Dual Action
This dual-action approach ensures that blood vessels are not only capable of adjusting their diameter for optimal blood flow but are also strong, resilient, and less prone to damage and inflammation.
Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of horse chestnut complement arginine’s cardiovascular benefits by protecting the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels. This protection can lead to stopping endothelial dysfunction, a precursor to atherosclerosis and other circulatory diseases. By stopping oxidative damage, the combination of arginine and horse chestnut supports the integrity of the inner veins, enhancing its capacity to produce nitric oxide and maintain vascular health.
In summary, while arginine alone offers significant benefits for enhancing nitric oxide production and improving vasodilation, it may not provide complete support for the multifaceted aspects of vascular health. Incorporating horse chestnut into a supplementation regimen that includes arginine can offer a more basic approach to maintaining and improving vascular health. This combination not only optimizes blood flow but also addresses the structural and functional needs of blood vessels, offering a comprehensive strategy for cardiovascular wellness.
Reason 4: Better Nitric Oxide Production with Vitamin D Supplementation: Stop Taking Arginine Alone
Vitamin D’s relationship with arginine extends beyond basic nutritional synergy, directly impacting the efficiency of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), the enzyme responsible for NO production from arginine. This interaction is crucial for understanding how the combination of arginine and vitamin D can significantly amplify and promote cardiovascular health, immune function, and overall well-being.
Vitamin D has been shown to enhance the expression and activity of nitric oxide synthase, thereby increasing the conversion of arginine into nitric oxide and this increase in nitric oxide availability is vital for vasodilation, which improves blood flow and reduces blood pressure, supporting your heart.
More NO
The enhancement of NO production by vitamin D not only increases the heart health benefits provided by arginine but also supports the function of the inner lining of blood vessels, further protecting against arterial stiffness and cardiovascular disease.
The synergy between vitamin D and arginine in creating higher nitric oxide levels has broader health implications as well, especially for your immune system and bone health. Elevated NO levels can improve immune response by supporting the body’s defense mechanisms against diseases. Nitric oxide acts as a signaling molecule in the immune system, managing various processes involved in the immune response. Vitamin D, well-recognized for its role in supporting immune function and reducing inflammation, works in concert with arginine-derived NO to create a more effective immune response.
In terms of bone health, the improved blood flow resulting from increased nitric oxide production ensures that nutrients essential for bone maintenance, including calcium and phosphate, are efficiently delivered and utilized in the body.
Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D plays a direct role in calcium absorption and bone mineralization, making its combination with arginine a strategic approach to supporting skeletal health and heart health.
Arguing for the effectiveness of taking arginine with vitamin D rests on understanding these mechanisms as well as vitamin D’s ability to increase nitric oxide synthase and increase nitric oxide production from arginine. This provides a compelling reason to combine Vit D for improved health outcomes. This synergy not only enhances cardiovascular benefits by improving vascular function and reducing blood pressure but also supports robust immune function and contributes to the maintenance of healthy bones.
The combination of arginine and vitamin D offers a potent approach to health supplementation, with vitamin D significantly enhancing the conversion of arginine into nitric oxide and thereby amplifying the benefits of arginine supplementation. This partnership between vitamin D and arginine underscores the importance of a natural approach to supplementation, where the combined effects of nutrients are leveraged to achieve the best health outcomes.
Reason 5: Reduced Antioxidant Protection
Antioxidants play a pivotal role in safeguarding the body against oxidation, a condition characterized by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage your cells, contributing to aging and various diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer, obviously things no one wants!
Antioxidants neutralize these nasty free radicals, thus protecting the body from damage. While arginine is known for its cardiovascular and immune system benefits, its antioxidant potential can be significantly improved when combined with vitamins E and C, both of which are powerful antioxidants. Also antioxidants make the nitric oxide molecule last longer, so they boost nitric oxides lifespan, and therefore effect! Yet another good reason you want to stop taking arginine by itself!
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that protects cell membranes from cellular damage by reacting with free radicals, which prevents the propagation of free radical damage within the body. This vitamin is particularly effective in protecting against lipid peroxidation, a process that can compromise cell membrane integrity and function. By maintaining cell membrane health, vitamin E supports the optimal functioning of cells, including those involved in the synthesis and utilization of arginine.
Vitamin C, a water-soluble antioxidant, complements vitamin E by neutralizing free radicals in the aqueous environments of the body. Furthermore, vitamin C can regenerate oxidized vitamin E, thereby restoring its antioxidant capacity making this a synergistic interaction that enhances the body’s overall antioxidant defense system.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C also plays a crucial role in the synthesis of collagen, a protein essential for the maintenance of blood vessels, skin, and connective tissues. The presence of adequate vitamin C can thus support the structural health of blood vessels, ensuring a conducive environment for arginine’s cardiovascular benefits.
The combination of arginine with vitamins E and C offers a multi-faceted approach to combating oxidative stress and supporting your health. Arginine, through its role in nitric oxide production, can improve vascular health and support the delivery of nutrients, including antioxidants, to tissues throughout the body while, vitamins E and C directly neutralize free radicals and protect against cellular damage. This collective action increases the antioxidant potential of these nutrients and also enhances their individual benefits. These benefits being mostly related to cardiovascular health, immune function, and tissue repair.
Advocating for the combination of arginine with vitamins E and C is grounded in the understanding that optimal personal health outcomes are often achieved through synergistic nutritional strategies.
This approach leverages the complementary actions of arginine and antioxidants to fortify the body’s defenses against disease, thereby supporting overall health and well-being.
By incorporating these nutrients into a comprehensive supplementation regimen, you can harness a more potent antioxidant defense, offering broader protection against damage and its associated health risks.

Coronary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil
All about The Coronary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil Study.
The Evolution of Health Management Strategies
In the quest to combat cardiovascular health issues and diabetes, the synergy between diet and exercise has been super important. Traditionally, the focus has been primarily on weight loss through caloric restriction and increased physical activity. IN other words, less food, more exercise.
However, recent advancements in health research have shifted the paradigm towards a broader, more nuanced understanding. The need for lifestyle modification’s in health optimization has become clear. Many studies such as the Coronary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil and Cardiovascular Prevention (CORDIOPREV) are now highlighting many new ideas. For one, the importance of not just how much we eat or how much we weigh, but what we eat and how our hearts function. These insights mark a significant departure from conventional wisdom. This new outlook suggests a complex interplay of factors contributing to cardiovascular health and diabetes management beyond simple weight metrics.
Understanding the Study’s Core Aims
The CORDIOPREV study delves deep into the realm of dietary interventions. It brings a keen focus to preventing and managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Unlike traditional approaches that prioritize weight loss as the main goal, this study examines the impact of diet quality. Specifically a Mediterranean diet enriched with olive oil—and its effects on cardiovascular outcomes. By contrasting these dietary interventions with standard low-fat diets, the research provides invaluable insights. One of the insights is how enhancing diet quality and improving cardiorespiratory fitness can serve as potent alternatives or complements to the weight-centric strategies of the past.
This introduction and study overview aim to set the stage for a detailed exploration of how modern research is reshaping our approach to health management through diet and exercise.
The Importance of Diet Quality in Managing Health
Diet quality plays a crucial role in the prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Studies have consistently shown that nutrient-dense diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The Mediterranean diet, in particular, has been extensively studied for its benefits in improving heart health and glycemic control. This dietary pattern is high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil. It also includes moderate amounts of fish and poultry, and limits the intake of red meat and processed foods.
Scientific Findings on Diet Quality
Research indicates that the Mediterranean diet and other high-quality dietary patterns can lower the risk of CVD and T2DM by improving lipid profiles, reducing inflammation, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and promoting a healthy body weight. A study involving the Coronary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil and Cardiovascular Prevention (CORDIOPREV) trial demonstrated a significant reduction in major CVD events among participants following a Mediterranean diet enriched with olive oil compared to those on a low-fat diet.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Diet Quality
- Start with Vegetables and Fruits: Aim to fill half of your plate with a variety of colorful vegetables and fruits at every meal. These are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains over refined grains. Examples include whole wheat, brown rice, oats, quinoa, and barley.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats in your diet, such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Select Lean Proteins: Focus on lean protein sources like fish, poultry, legumes, and low-fat dairy products.
- Limit Added Sugars and Processed Foods: Reduce the intake of foods high in added sugars and heavily processed foods to minimize empty calories and unhealthy fats.
The Role of Exercise and Cardiorespiratory Fitness
Evidence Supporting Cardiorespiratory Fitness
Improved cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is associated with a lower risk of CVD and T2DM. CRF refers to the efficiency of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems in supplying oxygen to the muscles during sustained physical activity. High levels of CRF are linked to reduced body fat, improved insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, and a healthier lipid profile. Regular physical activity is the most effective way to enhance CRF, with benefits extending beyond physical health to include mental and emotional well-being.
Integrating Physical Activity for Better Health
Incorporating regular physical activity into one’s routine is essential for improving CRF and overall health. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week, or a combination of both. This can include activities such as walking, cycling, swimming, running, or group exercise classes. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises at least two days per week can further improve muscle strength, bone health, and metabolic function.
Practical Suggestions for Enhancing Physical Activity
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with manageable goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities.
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Engaging in exercises that you find enjoyable increases the likelihood of consistency and long-term commitment.
- Incorporate Activity into Daily Life: Look for opportunities to be more active throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking or biking for short trips, or standing up and moving during breaks at work.
- Stay Motivated: Setting goals, tracking progress, and having an exercise buddy can help keep you motivated.
Improving health through diet quality and physical activity is a multifaceted approach that requires commitment and consistency. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and maintaining an active lifestyle, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of chronic diseases and enhance their quality of life.
Rethinking Salt and Heart Health: New Insights
For decades, common table salt has been cast as a major villain in the narrative of cardiovascular health. People interested in personal health and the like have avoided it. Today health professionals and dietary guidelines are cautioning against its excessive consumption. This is due mainly to the belief that it directly contributes to heart disease, hypertension, and stroke.
The conventional wisdom held that salt, or more specifically, the sodium it contains, was a primary culprit in raising blood pressure. This in turn is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease and something to be avoided by health conscious people. This stance led to widespread efforts to minimize salt intake as a preventative measure against heart-related conditions.
Historically, the relationship between salt and heart health was seen as straightforward. High salt intake was thought to increase blood pressure, which in turn, raised the risk of heart disease. This commonly held belief was supported by numerous studies and health organizations worldwide. They in turn advocated for reduced sodium diets as part of a heart-healthy lifestyle. Public health campaigns and dietary guidelines reflected this stance. It was common to hear them urging people to limit their consumption of salt-rich foods. People were warned about the dangers of the sodium content in processed foods and restaurant meals.
No One Size Fits All
However, as we shall see, recent research has begun to paint a more complex picture of the role of salt in cardiovascular health. Studies emerging in the last decade have challenged the one-size-fits-all approach to salt consumption. They are now suggesting that the impact of salt on heart health may not be nearly as detrimental for everyone as previously thought. These studies indicate that the relationship between salt intake and heart disease is more nuanced. It depends more on individual differences in salt sensitivity, genetic factors, and overall dietary patterns to name just a few variables.
One pivotal area of new research focuses on the concept of salt sensitivity. This sensitivity refers to the variation in how individuals’ blood pressure responds to salt intake. Some people experience significant increases in blood pressure with higher salt consumption. Others people however, show little to no change (salt-resistant individuals). This variability suggests that blanket recommendations for salt intake might not be appropriate for everyone. Again underscoring the need for personalized dietary advice based on individual health profiles and genetic predispositions.
Salt Studies
Recent studies have also explored the potential benefits of salt in the diet. Salt plays a crucial role in bodily functions. They include fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction. It is also an essential electrolyte that helps with hydration and cardiovascular function. The nuanced view acknowledges that while excessive salt intake can be harmful. This is especially so for those with hypertension or pre-existing heart conditions. Moderate consumption within a balanced diet however, might not pose the same level of risk for healthy individuals.
The evolving perspective on salt and heart health is also prompting a reevaluation of how dietary guidelines are formulated. Instead of strict limits on salt intake for the entire population, some researchers are advocating for guidelines. These guidelines take into consideration the complexity of individual health needs and the overall dietary context. For example, the quality of the diet as a whole—rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins—may mitigate the potential negative effects of a higher salt intake.
A More Nuanced Approach
This shift towards a more nuanced understanding of salt’s impact on heart health emphasizes the importance of considering individual differences, the role of other dietary factors, and the balance of risks and benefits when making dietary recommendations. It reflects a broader trend in nutrition science towards personalized nutrition and the recognition that dietary advice must be adaptable to meet the diverse needs of the population.

Debunking Myths About Salt and Heart Health
The common narrative around salt and its effects on heart health has been a point of contention and misunderstanding within both the medical community and public perception for decades on end. Historically, salt has been labeled as harmful, primarily due to its association with high blood pressure, a well known risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
This belief and ubiquitous perspective was largely influenced by early observational studies and clinical trials that showed a reduction in blood pressure following a decrease in salt intake. As a result, dietary guidelines worldwide have recommended low-sodium diets as a universal strategy for reducing heart disease risk.
Historical Context of Salt’s Harmful Label
The view of salt consumption being a bad thing began taking shape in the latter half of the 20th century when researchers first started linking high sodium intake with elevated blood pressure. Public health policies were subsequently influenced by these findings, leading to the widespread promotion of salt-reduction strategies to combat heart disease and a heck of a lot of bad press for salt and sodium. The simplicity of the message – less salt equals better heart health – was appealing for its ease of understanding and implementation. However, this approach failed to account for individual variability and the complexity of dietary patterns contributing to cardiovascular health and is more “truthy” and truth.
Recent Research Challenges the Old Narrative
In recent years, a growing body of clinical research has begun to challenge the traditional dogma on salt. The idea that all individuals benefit from reducing salt intake is under attack. A seminal turning point came with the recent publication of studies. These studies are suggesting that the relationship between salt and heart health is not straightforward. For example, a series of articles published in the “New England Journal of Medicine” in 2014 highlighted the potential risks of both high and low sodium intake. These indicate and suggest a U-shaped relationship between salt consumption and health outcomes. This means that both excessive and insufficient salt intake could be associated with adverse health effects.
Moreover, the PURE (Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology) study, one of the largest epidemiological studies to date, found that the association between sodium intake and cardiovascular events, as well as mortality, followed a J-shaped curve. This research indicated that while very high sodium intake was linked to increased heart disease risk, moderate intake was not, and very low intake might even be harmful.
Examples of Non-linear Relationship Studies
These findings underscore the complexity of the relationship between salt intake and heart disease risk. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the “Lancet” in 2016 analyzed data from over 130,000 individuals and concluded that low sodium intake was associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and death in individuals without hypertension. However this study has come under serious attack.
Conversely, only high sodium intake (exceeding 6 grams per day) was associated with an increased risk among those with high blood pressure.
Such evidence suggests a need to revisit and refine public health guidelines concerning salt consumption. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, there’s a growing consensus among scientists and nutrition experts for guidelines that consider individual health status, dietary context, and even genetic predispositions.
A Shift In Understanding
The shift in understanding underscores the importance of nuanced dietary advice and the need for continued research. We need to better identify those who may benefit from salt reduction . We also must identify those for whom too little salt may be just as concerning. This evolving narrative challenges long-standing dietary dogmas. It also opens the door for more personalized nutrition strategies that better reflect the complexities of human health.
Balancing Salt Intake for Optimal Heart Health
Achieving a balanced salt intake is crucial for maintaining heart health. Without unnecessarily restricting dietary pleasures, salt after all tastes good. Moderation and mindful consumption are key, alongside an understanding of how dietary quality and the source of salt can influence overall health outcomes.
Guidelines for Moderating Salt Consumption
- Understand Individual Needs: Recognize personal health factors, such as blood pressure levels and any history of heart disease, to tailor salt intake accordingly, you may or may not be sensitive to salt so some personal monitoring is advised.
- Aim for Moderation: The American Heart Association recommends no more than 2,300 milligrams a day, moving toward an ideal limit of about 1,500 mg per day for most adults.
The Role of Diet Quality and Salt Source
- Prioritize Whole Foods: Focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, which naturally contain lower amounts of sodium, while at the same time, not overdoing it on the sugars.
- Limit Processed Foods: These are the primary sources of high sodium in the diet, often containing much more salt than their natural or homemade counterparts, and are bad for you in so many other ways due to trans-fats and other ingredients.
- Choose Natural Salt Sources: When adding salt to foods, opt for unprocessed or minimally processed salts. Be mindful that all forms of salt have similar sodium content by weight, but natural sources may offer trace minerals.
Tips for Adding Flavor Without Excessive Salt
- Use Herbs and Spices: Enhance flavor with a variety of herbs, spices, citrus, vinegar, and garlic instead of relying solely on salt, there are many other flavors to choose from!
- Experiment with Salt-Free Seasoning Blends: Many blends can provide depth of flavor to dishes without adding sodium.
- Balance with Acidity: A splash of lemon juice or vinegar can brighten dishes, often reducing the need for added salt.
Practical Tips for Managing Salt Intake
Managing salt intake does not have to mean sacrificing flavor or enjoyment of food. By adopting some practical strategies, it’s possible to reduce sodium consumption while still enjoying a rich and varied diet.
Strategies for Reducing Reliance on Processed Foods
- Cook More at Home: Preparing meals from scratch gives you control over the amount of salt used.
- Choose Fresh or Frozen Produce: Opt for fresh or frozen fruits and vegetables, which are low in sodium, over canned varieties that may contain added salt.
- Select Low-Sodium Products: When buying processed foods, look for items labeled “low sodium,” “reduced sodium,” or “no salt added.”
How to Read Food Labels for Better Sodium Management
- Check the Sodium Content: Pay attention to the milligrams of sodium per serving and the number of servings per package.
- Understand Sodium Descriptors: Learn what terms like “sodium-free,” “very low sodium,” and “low sodium” mean in terms of actual sodium content.
Incorporating Potassium-Rich Foods to Balance Sodium Intake
- Eat Potassium-Rich Foods: Foods high in potassium, such as bananas, potatoes, spinach, and beans, can help counteract the effects of sodium and support healthy blood pressure.
- Understand the Sodium-Potassium Balance: A diet high in potassium can help to mitigate some of the negative effects of high sodium intake on blood pressure.
By embracing these guidelines and tips, you can find a healthy balance in your salt intake that supports heart health without diminishing the joy of eating. This approach encourages a more holistic view of diet, focusing on overall nutritional balance and the quality of ingredients, rather than simply cutting out salt.